File size: 6,453 Bytes
a8e503d aa16861 a8e503d d6a43c6 a8e503d 82698e0 a8e503d ab56130 a8e503d 82698e0 a8e503d 23004da a8e503d b5ac7a2 a8e503d 1e33e79 a8e503d ab56130 a8e503d |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 |
---
datasets:
- BatsResearch/ctga-v1
language:
- en
library_name: transformers
pipeline_tag: text2text-generation
tags:
- data generation
license: apache-2.0
---
# Model Card for bonito
<!-- Provide a quick summary of what the model is/does. -->
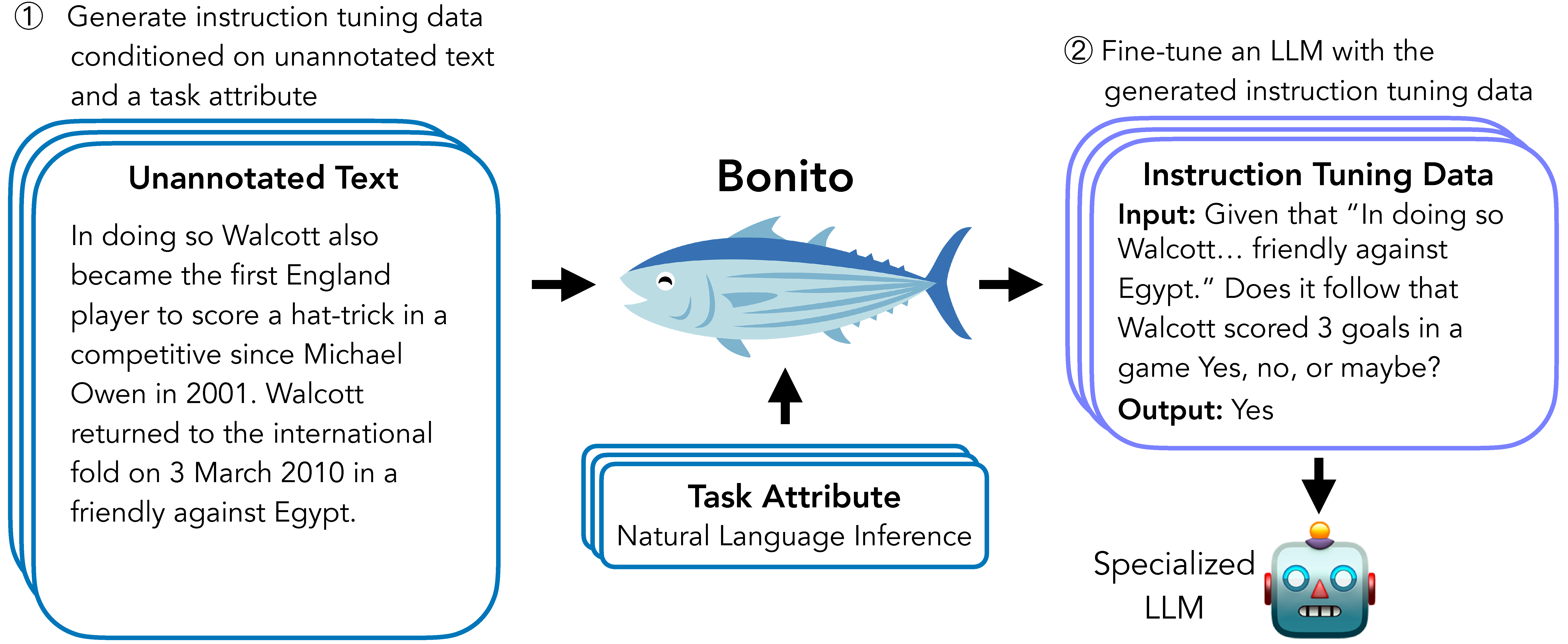
Bonito is an open-source model for conditional task generation: the task of converting unannotated text into task-specific training datasets for instruction tuning.
## Model Details
### Model Description
<!-- Provide a longer summary of what this model is. -->
Bonito can be used to create synthetic instruction tuning datasets to adapt large language models on users' specialized, private data.
In our [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.18334), we show that Bonito can be used to adapt both pretrained and instruction tuned models to tasks without any annotations.
- **Developed by:** Nihal V. Nayak, Yiyang Nan, Avi Trost, and Stephen H. Bach
- **Model type:** MistralForCausalLM
- **Language(s) (NLP):** English
- **License:** Apache 2.0
- **Finetuned from model:** `mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1`
### Model Sources
<!-- Provide the basic links for the model. -->
- **Repository:** [https://github.com/BatsResearch/bonito](https://github.com/BatsResearch/bonito)
- **Paper:** [Learning to Generate Instruction Tuning Datasets for
Zero-Shot Task Adaptation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.18334)
## Uses
<!-- Address questions around how the model is intended to be used, including the foreseeable users of the model and those affected by the model. -->
### Direct Use
<!-- This section is for the model use without fine-tuning or plugging into a larger ecosystem/app. -->
To easily generate synthetic instruction tuning datasets, we recommend using the [bonito](https://github.com/BatsResearch/bonito) package built using the `transformers` and the `vllm` libraries.
```python
from bonito import Bonito
from vllm import SamplingParams
from datasets import load_dataset
# Initialize the Bonito model
bonito = Bonito("BatsResearch/bonito-v1")
# load dataaset with unannotated text
unannotated_text = load_dataset(
"BatsResearch/bonito-experiment",
"unannotated_contract_nli"
)["train"].select(range(10))
# Generate synthetic instruction tuning dataset
sampling_params = SamplingParams(max_tokens=256, top_p=0.95, temperature=0.5, n=1)
synthetic_dataset = bonito.generate_tasks(
unannotated_text,
context_col="input",
task_type="nli",
sampling_params=sampling_params
)
```
### Out-of-Scope Use
<!-- This section addresses misuse, malicious use, and uses that the model will not work well for. -->
Our model is trained to generate the following task types: summarization, sentiment analysis, multiple-choice question answering, extractive question answering, topic classification, natural language inference, question generation, text generation, question answering without choices, paraphrase identification, sentence completion, yes-no question answering, word sense disambiguation, paraphrase generation, textual entailment, and
coreference resolution.
The model might not produce accurate synthetic tasks beyond these task types.
## Bias, Risks, and Limitations
<!-- This section is meant to convey both technical and sociotechnical limitations. -->
**Limitations**
Our work relies on the availability of large amounts of unannotated text.
If only a small quantity of unannotated text is present, the target language model, after adaptation, may experience a drop in performance.
While we demonstrate positive improvements on pretrained and instruction-tuned models, our observations are limited to the three task types (yes-no question answering, extractive question answering, and natural language inference) considered in our paper.
**Risks**
Bonito poses risks similar to those of any large language model.
For example, our model could be used to generate factually incorrect datasets in specialized domains.
Our model can exhibit the biases and stereotypes of the base model, Mistral-7B, even after extensive supervised fine-tuning.
Finally, our model does not include safety training and can potentially generate harmful content.
### Recommendations
<!-- This section is meant to convey recommendations with respect to the bias, risk, and technical limitations. -->
We recommend users thoroughly inspect the generated tasks and benchmark performance on critical datasets before deploying the models trained with the synthetic tasks into the real world.
## Training Details
### Training Data
<!-- This should link to a Dataset Card, perhaps with a short stub of information on what the training data is all about as well as documentation related to data pre-processing or additional filtering. -->
To train Bonito, we create a new dataset called conditional task generation with attributes by remixing existing instruction tuning datasets.
See [ctga-v1](https://huggingface.co/datasets/BatsResearch/ctga-v1) for more details.
### Training Procedure
<!-- This relates heavily to the Technical Specifications. Content here should link to that section when it is relevant to the training procedure. -->
#### Training Hyperparameters
- **Training regime:** <!--fp32, fp16 mixed precision, bf16 mixed precision, bf16 non-mixed precision, fp16 non-mixed precision, fp8 mixed precision -->
We train the model using [Q-LoRA](https://github.com/artidoro/qlora) by optimizing the cross entropy loss over the output tokens.
The model is trained for 100,000 steps.
The training takes about 4 days on four GPUs to complete.
We use the following hyperparameters:
- Q-LoRA rank (r): 64
- Q-LoRA scaling factor (alpha): 4
- Q-LoRA dropout: 0
- Optimizer: Paged AdamW
- Learning rate scheduler: linear
- Max. learning rate: 1e-04
- Min. learning rate: 0
- Weight decay: 0
- Dropout: 0
- Max. gradient norm: 0.3
- Effective batch size: 16
- Max. input length: 2,048
- Max. output length: 2,048
- Num. steps: 100,000
## Citation
<!-- If there is a paper or blog post introducing the model, the APA and Bibtex information for that should go in this section. -->
```
@article{bonito:arxiv24,
Author = {Nihal V. Nayak and Yiyang Nan and Avi Trost and Stephen H. Bach},
Title = {Learning to Generate Instruction Tuning Datasets for Zero-Shot Task Adaptation},
Volume = {arXiv:2402.18334 [cs.CL]},
Year = {2024}}
``` |