File size: 6,025 Bytes
c25a5d9 004e350 5cab3a3 004e350 1e9a811 004e350 1e9a811 11f7b91 1e9a811 11f7b91 1e9a811 004e350 1e9a811 004e350 1e9a811 004e350 1e9a811 004e350 1e9a811 004e350 1e9a811 d2195a8 004e350 1e9a811 004e350 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 |
---
license: mit
---
# ERNIE-Code
[ERNIE-Code: Beyond English-Centric Cross-lingual Pretraining for Programming Languages](https://aclanthology.org/2023.findings-acl.676.pdf)
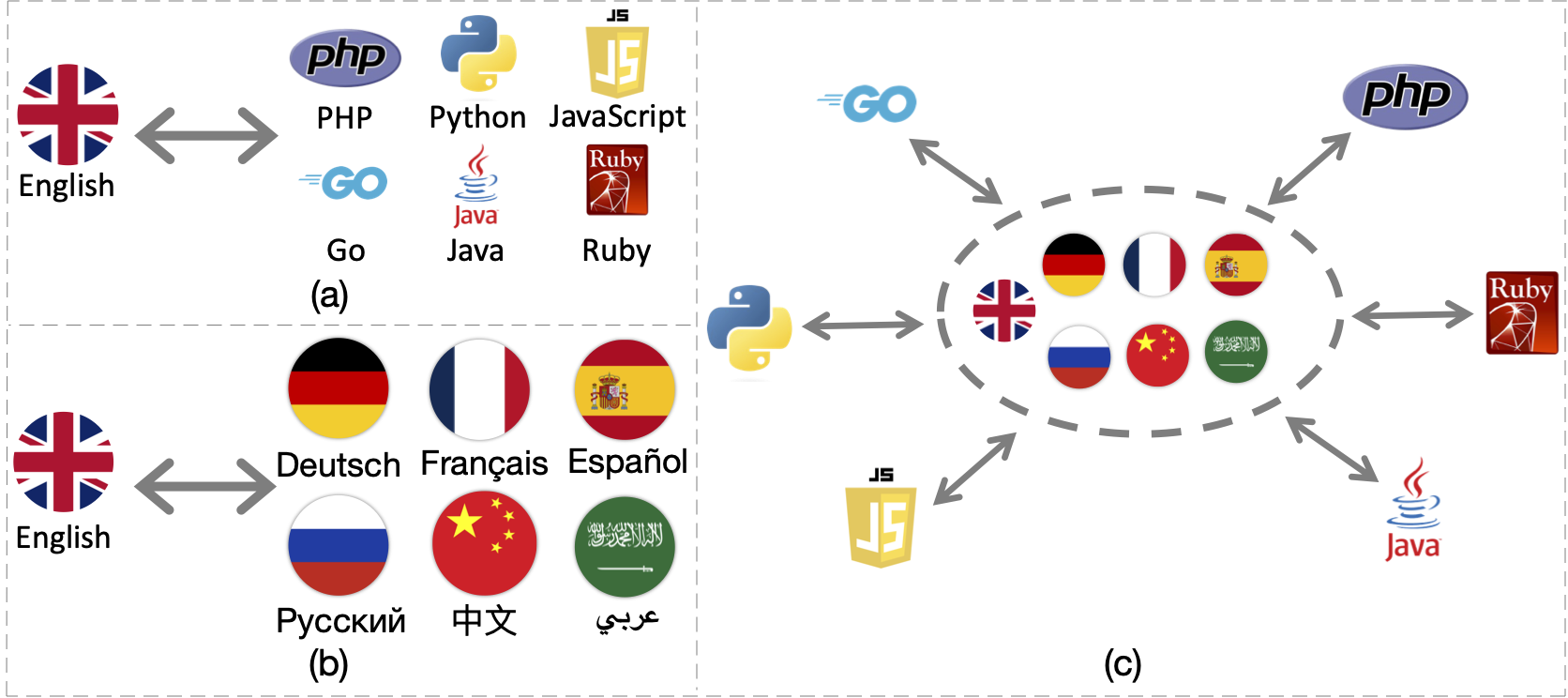
ERNIE-Code is a unified large language model (LLM) that connects 116 natural languages with 6 programming languages. We employ two pre-training methods for universal cross-lingual pre-training: span-corruption language modeling that learns patterns from monolingual NL or PL; and pivot-based translation language modeling that relies on parallel data of many NLs and PLs. Extensive results show that ERNIE-Code outperforms previous multilingual LLMs for PL or NL across a wide range of end tasks of code intelligence, including multilingual code-to-text, text-to-code, code-to-code, and text-to-text generation. We further show its advantage of zero-shot prompting on multilingual code summarization and text-to-text translation.
[ACL 2023 (Findings)](https://aclanthology.org/2023.findings-acl.676/) | [arXiv](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.06742)
### Usage
```python
import torch
from transformers import (
AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM,
AutoModelForCausalLM,
AutoTokenizer
)
model_name = "baidu/ernie-code-560m"
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
# note that you can use aforementioned `clean_up_code_spaces` to proprocess the code
def format_code_with_spm_compatablity(line: str):
format_dict = {
" " : "<|space|>"
}
tokens = list(line)
i = 0
while i < len(tokens):
if line[i] == "\n":
while i+1 < len(tokens) and tokens[i+1] == " ":
tokens[i+1] = format_dict.get(" ")
i += 1
i += 1
formatted_line = ''.join(tokens)
return formatted_line
"""
TYPE="code" # define input type in ("code", "text")
input="arr.sort()"
prompt="translate python to java: \n%s" % (input) # your prompt here
"""
TYPE="text" # define input type in ("code", "text")
input="quick sort"
prompt="translate English to Japanese: \n%s" % (input) # your prompt here
assert TYPE in ("code", "text")
# preprocess for code input
if TYPE=="code":
prompt = format_code_with_spm_compatablity(prompt)
model_inputs = tokenizer(prompt, max_length=512, padding=False, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
model = model.cuda() # by default
input_ids = model_inputs.input_ids.cuda() # by default
attention_mask = model_inputs.attention_mask.cuda() # by default
output = model.generate(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask,
num_beams=5, max_length=20) # change to your needs
# Ensure to customize the post-processing of `clean_up_code_spaces` output according to specific requirements.
output = tokenizer.decode(output.flatten(), skip_special_tokens=True)
# post-process the code generation
def clean_up_code_spaces(s: str):
# post process
# ===========================
new_tokens = ["<pad>", "</s>", "<unk>", "\n", "\t", "<|space|>"*4, "<|space|>"*2, "<|space|>"]
for tok in new_tokens:
s = s.replace(f"{tok} ", tok)
cleaned_tokens = ["<pad>", "</s>", "<unk>"]
for tok in cleaned_tokens:
s = s.replace(tok, "")
s = s.replace("<|space|>", " ")
return s
output = [clean_up_code_spaces(pred) for pred in output]
```
You can adapt [seq2seq translation code](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/translation) for finetuning.
You can also check the official inference code on [PaddleNLP](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/blob/develop/model_zoo/ernie-code/README.en.md).
### Zero-shot Examples
- Multilingual code-to-text generation (zero-shot)
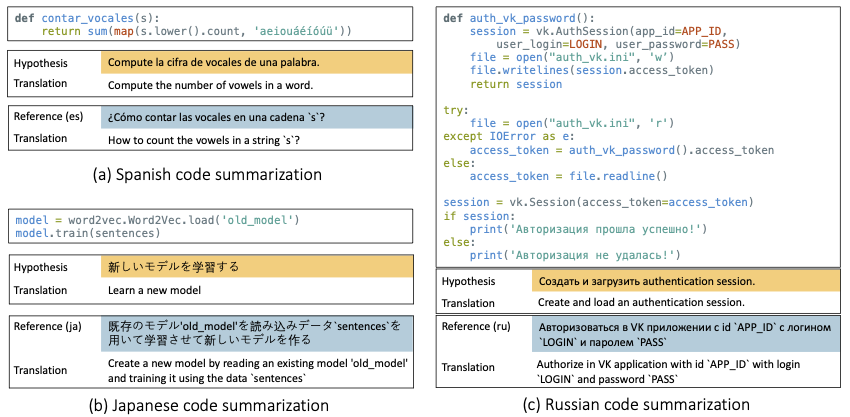

- Multilingual text-to-text translation (zero-shot)

## BibTeX
```
@inproceedings{chai-etal-2023-ernie,
title = "{ERNIE}-Code: Beyond {E}nglish-Centric Cross-lingual Pretraining for Programming Languages",
author = "Chai, Yekun and
Wang, Shuohuan and
Pang, Chao and
Sun, Yu and
Tian, Hao and
Wu, Hua",
booktitle = "Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2023",
month = jul,
year = "2023",
address = "Toronto, Canada",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2023.findings-acl.676",
pages = "10628--10650",
abstract = "Software engineers working with the same programming language (PL) may speak different natural languages (NLs) and vice versa, erecting huge barriers to communication and working efficiency. Recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of generative pre-training in computer programs, yet they are always English-centric. In this work, we step towards bridging the gap between multilingual NLs and multilingual PLs for large language models (LLMs). We release ERNIE-Code, a unified pre-trained language model for 116 NLs and 6 PLs. We employ two methods for universal cross-lingual pre-training: span-corruption language modeling that learns patterns from monolingual NL or PL; and pivot-based translation language modeling that relies on parallel data of many NLs and PLs. Extensive results show that ERNIE-Code outperforms previous multilingual LLMs for PL or NL across a wide range of end tasks of code intelligence, including multilingual code-to-text, text-to-code, code-to-code, and text-to-text generation. We further show its advantage of zero-shot prompting on multilingual code summarization and text-to-text translation. We release our code and pre-trained checkpoints.",
}
```
|