# OpenCLIP
[[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.01903) [[Colab]](https://colab.research.google.com/github/mlfoundations/open_clip/blob/master/docs/Interacting_with_open_clip.ipynb)
Welcome to an open source implementation of OpenAI's [CLIP](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020) (Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training).
The goal of this repository is to enable training models with contrastive image-text supervision, and to investigate their properties such as robustness to distribution shift. Our starting point is an implementation of CLIP that matches the accuracy of the original CLIP models when trained on the same dataset.
Specifically, a ResNet-50 model trained with our codebase on OpenAI's [15 million image subset of YFCC](https://github.com/openai/CLIP/blob/main/data/yfcc100m.md) achieves **32.7%** top-1 accuracy on ImageNet. OpenAI's CLIP model reaches **31.3%** when trained on the same subset of YFCC. For ease of experimentation, we also provide code for training on the 3 million images in the [Conceptual Captions](https://ai.google.com/research/ConceptualCaptions/download) dataset, where a ResNet-50x4 trained with our codebase reaches 22.2% top-1 ImageNet accuracy.
We further this with a replication study on a dataset of comparable size to OpenAI's. Using [LAION-400M](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.02114), we train CLIP with a
* ViT-B/32 and achieve an accuracy of **62.9%**, comparable to OpenAI's **63.2%**, zero-shot top-1 on ImageNet1k
* ViT-B/16 and achieve an accuracy of **67.1%**, comparable to OpenAI's **68.3%** (as measured here, 68.6% in paper)
* ViT-B/16+ 240x240 (~50% more FLOPS than B/16 224x224) and achieve an accuracy of **69.2%**
* ViT-L/14 and achieve an accuracy of **72.77%**, vs OpenAI's **75.5%** (as measured here, 75.3% in paper)
As we describe in more detail [below](#why-are-low-accuracy-clip-models-interesting), CLIP models in a medium accuracy regime already allow us to draw conclusions about the robustness of larger CLIP models since the models follow [reliable scaling laws](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.04649).
This codebase is work in progress, and we invite all to contribute in making it more acessible and useful. In the future, we plan to add support for TPU training and release larger models. We hope this codebase facilitates and promotes further research in contrastive image-text learning. Please submit an issue or send an email if you have any other requests or suggestions.
Note that portions of `src/open_clip/` modelling and tokenizer code are adaptations of OpenAI's official [repository](https://github.com/openai/CLIP).
## Approach
| 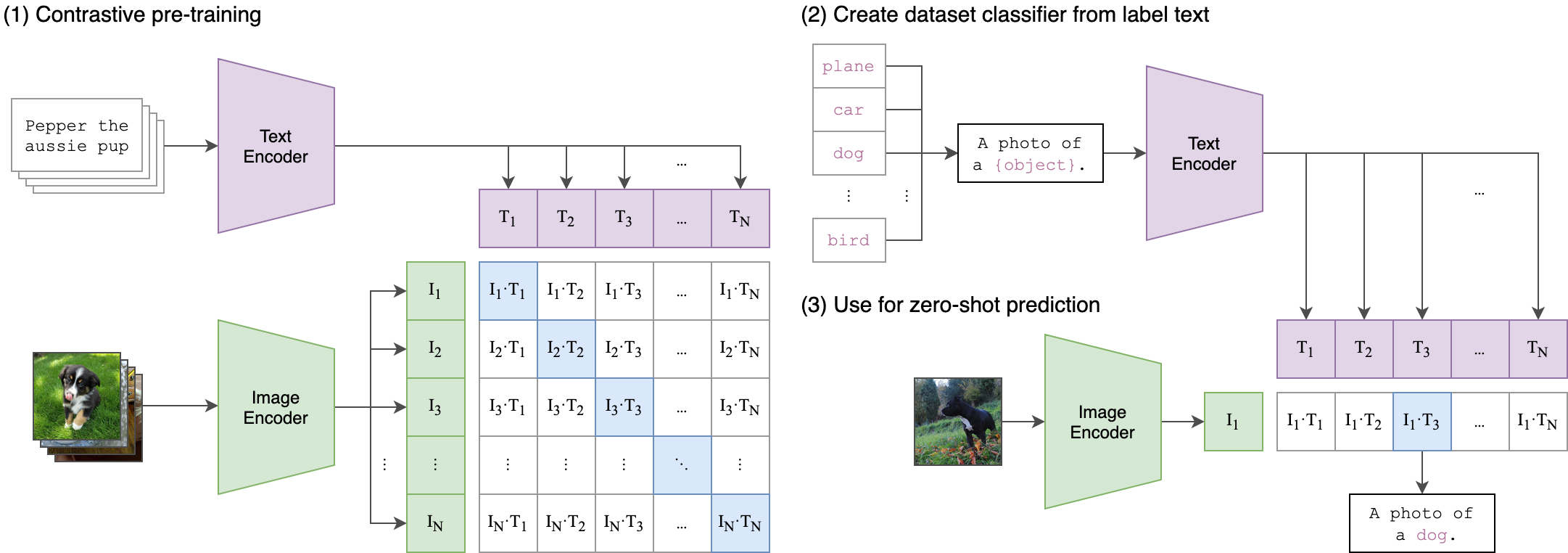 |
|:--:|
| Image Credit: https://github.com/openai/CLIP |
## Usage
```
pip install open_clip_torch
```
```python
import torch
from PIL import Image
import open_clip
model, _, preprocess = open_clip.create_model_and_transforms('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', pretrained='laion400m_e32')
image = preprocess(Image.open("CLIP.png")).unsqueeze(0)
text = open_clip.tokenize(["a diagram", "a dog", "a cat"])
with torch.no_grad():
image_features = model.encode_image(image)
text_features = model.encode_text(text)
image_features /= image_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
text_features /= text_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
text_probs = (100.0 * image_features @ text_features.T).softmax(dim=-1)
print("Label probs:", text_probs) # prints: [[1., 0., 0.]]
```
To compute billions of embeddings efficiently, you can use [clip-retrieval](https://github.com/rom1504/clip-retrieval) which has openclip support.
## Fine-tuning on classification tasks
This repository is focused on training CLIP models. To fine-tune a *trained* zero-shot model on a downstream classification task such as ImageNet, please see [our other repository: WiSE-FT](https://github.com/mlfoundations/wise-ft). The [WiSE-FT repository](https://github.com/mlfoundations/wise-ft) contains code for our paper on [Robust Fine-tuning of Zero-shot Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.01903), in which we introduce a technique for fine-tuning zero-shot models while preserving robustness under distribution shift.
## Data
### Conceptual Captions
OpenCLIP reads a CSV file with two columns: a path to an image, and a text caption. The names of the columns are passed as an argument to `main.py`.
The script `src/data/gather_cc.py` will collect the Conceptual Captions images. First, download the [Conceptual Captions URLs](https://ai.google.com/research/ConceptualCaptions/download) and then run the script from our repository:
```bash
python3 src/data/gather_cc.py path/to/Train_GCC-training.tsv path/to/Validation_GCC-1.1.0-Validation.tsv
```
Our training set contains 2.89M images, and our validation set contains 13K images.
### YFCC and other datasets
In addition to specifying the training data via CSV files as mentioned above, our codebase also supports [webdataset](https://github.com/webdataset/webdataset), which is recommended for larger scale datasets. The expected format is a series of `.tar` files. Each of these `.tar` files should contain two files for each training example, one for the image and one for the corresponding text. Both files should have the same name but different extensions. For instance, `shard_001.tar` could contain files such as `abc.jpg` and `abc.txt`. You can learn more about `webdataset` at [https://github.com/webdataset/webdataset](https://github.com/webdataset/webdataset). We use `.tar` files with 1,000 data points each, which we create using [tarp](https://github.com/webdataset/tarp).
You can download the YFCC dataset from [Multimedia Commons](http://mmcommons.org/).
Similar to OpenAI, we used a subset of YFCC to reach the aforementioned accuracy numbers.
The indices of images in this subset are in [OpenAI's CLIP repository](https://github.com/openai/CLIP/blob/main/data/yfcc100m.md).
## Training CLIP
### Setup Environment and Install dependencies
#### Conda
```bash
# Create a conda environment (heavily recommended)
conda create -n open_clip python=3.10
conda activate open_clip
```
Install conda PyTorch as per https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/
#### Virtualenv
openclip also can be used with virtualenv with these lines:
```
python3 -m venv .env
source .env/bin/activate
pip install -U pip
make install
```
Install pip PyTorch as per https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/
Test can be run with `make install-dev` then `make test`
#### Other dependencies
Install open_clip pacakge and remaining dependencies:
```bash
cd open_clip
python setup.py install
```
If you want to train models, you will also need to install the packages
from `requirements-training.txt`.
### Sample single-process running code:
```bash
python -m training.main \
--save-frequency 1 \
--zeroshot-frequency 1 \
--report-to tensorboard \
--train-data="/path/to/train_data.csv" \
--val-data="/path/to/validation_data.csv" \
--csv-img-key filepath \
--csv-caption-key title \
--imagenet-val=/path/to/imagenet/root/val/ \
--warmup 10000 \
--batch-size=128 \
--lr=1e-3 \
--wd=0.1 \
--epochs=30 \
--workers=8 \
--model RN50
```
Note: `imagenet-val` is the path to the *validation* set of ImageNet for zero-shot evaluation, not the training set!
You can remove this argument if you do not want to perform zero-shot evaluation on ImageNet throughout training. Note that the `val` folder should contain subfolders. If it doest not, please use [this script](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/soumith/imagenetloader.torch/master/valprep.sh).
### Multi-GPU and Beyond
This code has been battle tested up to 1024 A100s and offers a variety of solutions
for distributed training. We include native support for SLURM clusters.
As the number of devices used to train increases, so does the space complexity of
the the logit matrix. Using a naïve all-gather scheme, space complexity will be
`O(n^2)`. Instead, complexity may become effectively linear if the flags
`--gather-with-grad` and `--local-loss` are used. This alteration results in one-to-one
numerical results as the naïve method.
#### Single-Node
We make use of `torchrun` to launch distributed jobs. The following launches a
a job on a node of 4 GPUs:
```bash
cd open_clip/src
torchrun --nproc_per_node 4 -m training.main \
--train-data '/data/cc12m/cc12m-train-{0000..2175}.tar' \
--train-num-samples 10968539 \
--dataset-type webdataset \
--batch-size 320 \
--precision amp \
--workers 4 \
--imagenet-val /data/imagenet/validation/
```
#### Multi-Node
The same script above works, so long as users include information about the number
of nodes and host node.
```bash
cd open_clip/src
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 \
--rdzv_endpoint=$HOSTE_NODE_ADDR \
-m training.main \
--train-data '/data/cc12m/cc12m-train-{0000..2175}.tar' \
--train-num-samples 10968539 \
--dataset-type webdataset \
--batch-size 320 \
--precision amp \
--workers 4 \
--imagenet-val /data/imagenet/validation/
```
#### SLURM
This is likely the easiest solution to utilize. The following script was used to
train our largest models:
```bash
#!/bin/bash -x
#SBATCH --nodes=32
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:4
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=4
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=6
#SBATCH --wait-all-nodes=1
#SBATCH --job-name=open_clip
#SBATCH --account=ACCOUNT_NAME
#SBATCH --partition PARTITION_NAME
eval "$(/path/to/conda/bin/conda shell.bash hook)" # init conda
conda activate open_clip
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
export MASTER_PORT=12802
master_addr=$(scontrol show hostnames "$SLURM_JOB_NODELIST" | head -n 1)
export MASTER_ADDR=$master_addr
cd /shared/open_clip
export PYTHONPATH="$PYTHONPATH:$PWD/src"
srun --cpu_bind=v --accel-bind=gn python -u src/training/main.py \
--save-frequency 1 \
--report-to tensorboard \
--train-data="/data/LAION-400M/{00000..41455}.tar" \
--warmup 2000 \
--batch-size=256 \
--epochs=32 \
--workers=8 \
--model ViT-B-32 \
--name "ViT-B-32-Vanilla" \
--seed 0 \
--local-loss \
--gather-with-grad
```
### Resuming from a checkpoint:
```bash
python -m training.main \
--train-data="/path/to/train_data.csv" \
--val-data="/path/to/validation_data.csv" \
--resume /path/to/checkpoints/epoch_K.pt
```
### Loss Curves
When run on a machine with 8 GPUs the command should produce the following training curve for Conceptual Captions:
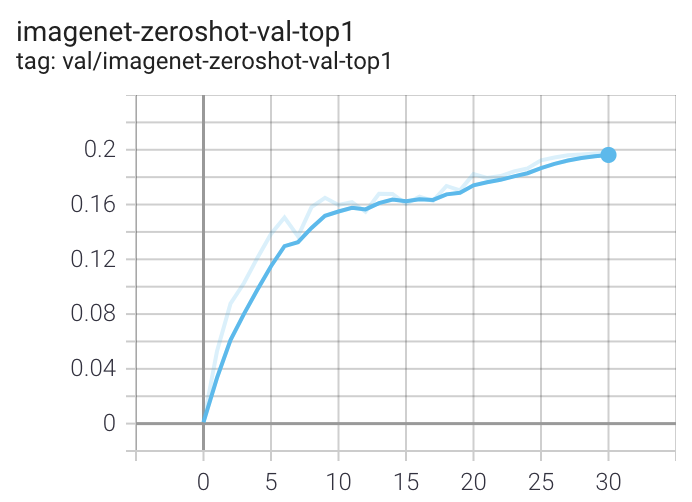
More detailed curves for Conceptual Captions are given at [/docs/clip_conceptual_captions.md](/docs/clip_conceptual_captions.md).
When training a RN50 on YFCC the same hyperparameters as above are used, with the exception of `lr=5e-4` and `epochs=32`.
Note that to use another model, like `ViT-B/32` or `RN50x4` or `RN50x16` or `ViT-B/16`, specify with `--model RN50x4`.
### Launch tensorboard:
```bash
tensorboard --logdir=logs/tensorboard/ --port=7777
```
## Evaluation / Zero-Shot
### Evaluating local checkpoint:
```bash
python -m training.main \
--val-data="/path/to/validation_data.csv" \
--model RN101 \
--pretrained /path/to/checkpoints/epoch_K.pt
```
### Evaluating hosted pretrained checkpoint on ImageNet zero-shot prediction:
```bash
python -m training.main \
--imagenet-val /path/to/imagenet/validation \
--model ViT-B-32-quickgelu \
--pretrained laion400m_e32
```
## Pretrained model details
### LAION-400M - https://laion.ai/laion-400-open-dataset
We are working on reproducing OpenAI's ViT results with the comparably sized (and open) LAION-400M dataset. Trained
weights may be found in release [v0.2](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/tag/v0.2-weights).
The LAION400M weights have been trained on the JUWELS supercomputer (see acknowledgements section below).
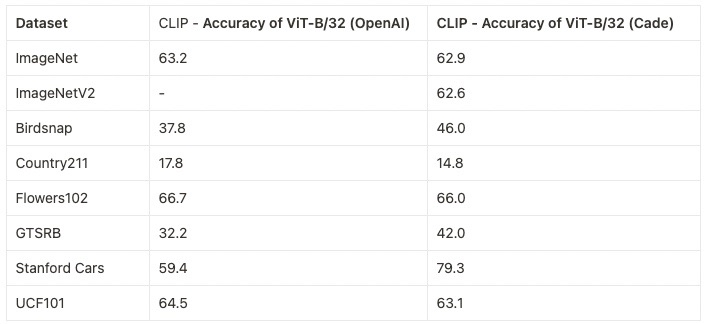
#### ViT-B/32 224x224
We replicate OpenAI's results on ViT-B/32, reaching a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot accuracy of 62.96%.
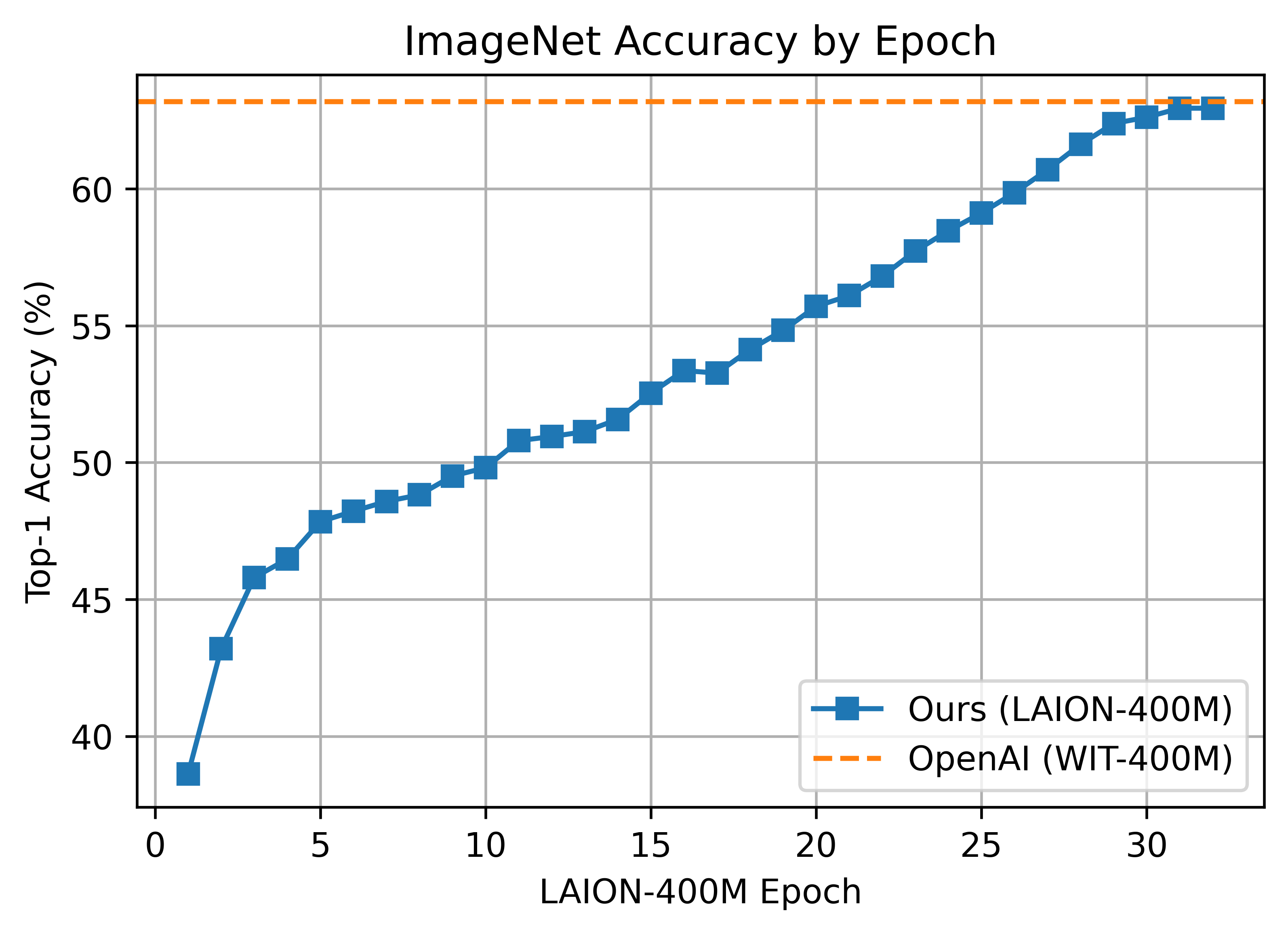 __Zero-shot comparison (courtesy of Andreas Fürst)__
__Zero-shot comparison (courtesy of Andreas Fürst)__
 ViT-B/32 was trained with 128 A100 (40 GB) GPUs for ~36 hours, 4600 GPU-hours. The per-GPU batch size was 256 for a global batch size of 32768. 256 is much lower than it could have been (~320-384) due to being sized initially before moving to 'local' contrastive loss.
#### ViT-B/16 224x224
The B/16 LAION400M training reached a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot validation score of 67.07.
ViT-B/32 was trained with 128 A100 (40 GB) GPUs for ~36 hours, 4600 GPU-hours. The per-GPU batch size was 256 for a global batch size of 32768. 256 is much lower than it could have been (~320-384) due to being sized initially before moving to 'local' contrastive loss.
#### ViT-B/16 224x224
The B/16 LAION400M training reached a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot validation score of 67.07.
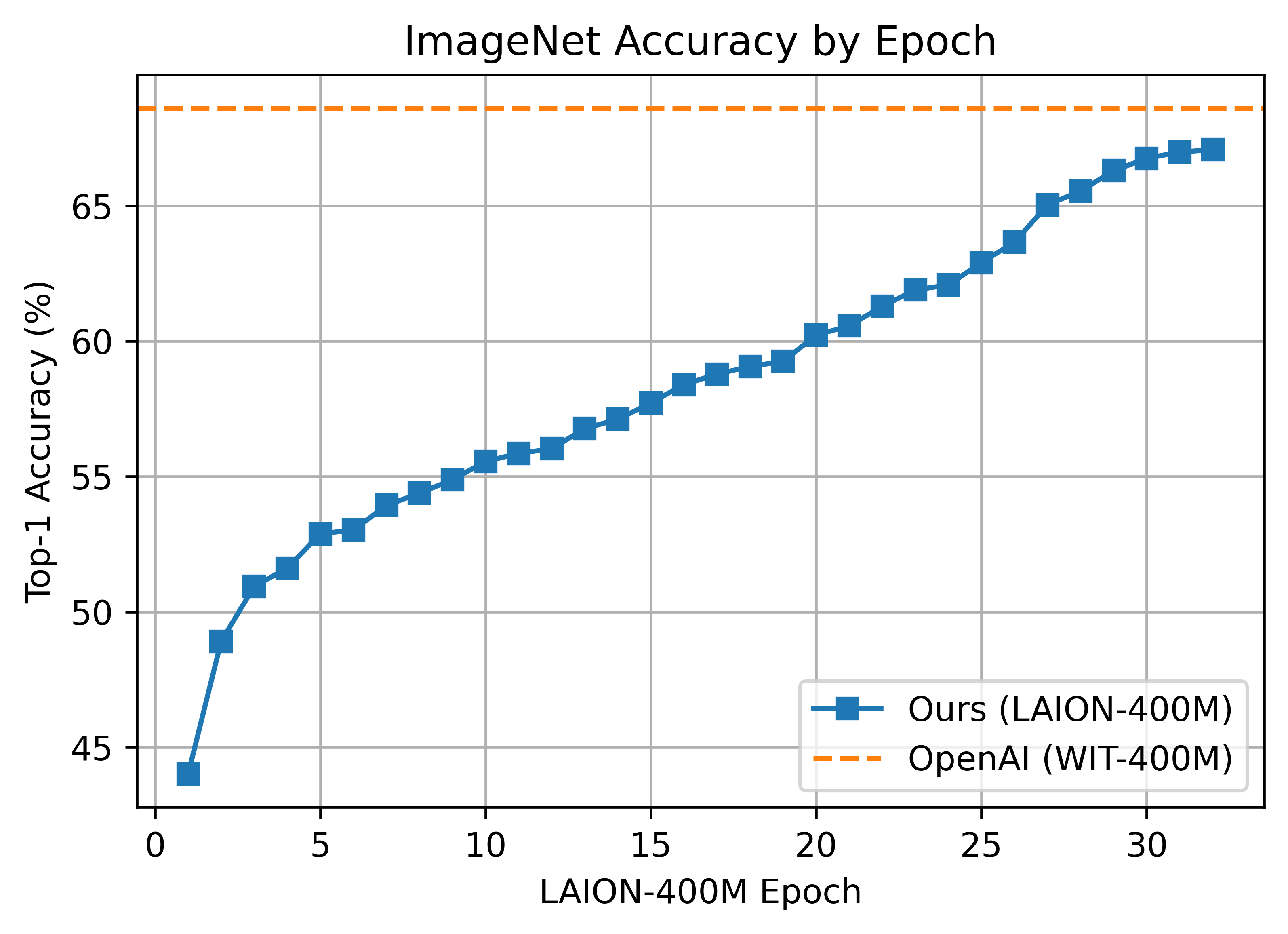 This was the first major train session using the updated webdataset 0.2.x code. A bug was found that prevented shards from being shuffled properly between nodes/workers each epoch. This was fixed part way through training (epoch 26) but likely had an impact.
ViT-B/16 was trained with 176 A100 (40 GB) GPUS for ~61 hours, 10700 GPU-hours. Batch size per GPU was 192 for a global batch size of 33792.
#### ViT-B/16+ 240x240
The B/16+ 240x240 LAION400M training reached a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot validation score of 69.21.
This model is the same depth as the B/16, but increases the
* vision width from 768 -> 896
* text width from 512 -> 640
* the resolution 224x224 -> 240x240 (196 -> 225 tokens)
This was the first major train session using the updated webdataset 0.2.x code. A bug was found that prevented shards from being shuffled properly between nodes/workers each epoch. This was fixed part way through training (epoch 26) but likely had an impact.
ViT-B/16 was trained with 176 A100 (40 GB) GPUS for ~61 hours, 10700 GPU-hours. Batch size per GPU was 192 for a global batch size of 33792.
#### ViT-B/16+ 240x240
The B/16+ 240x240 LAION400M training reached a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot validation score of 69.21.
This model is the same depth as the B/16, but increases the
* vision width from 768 -> 896
* text width from 512 -> 640
* the resolution 224x224 -> 240x240 (196 -> 225 tokens)
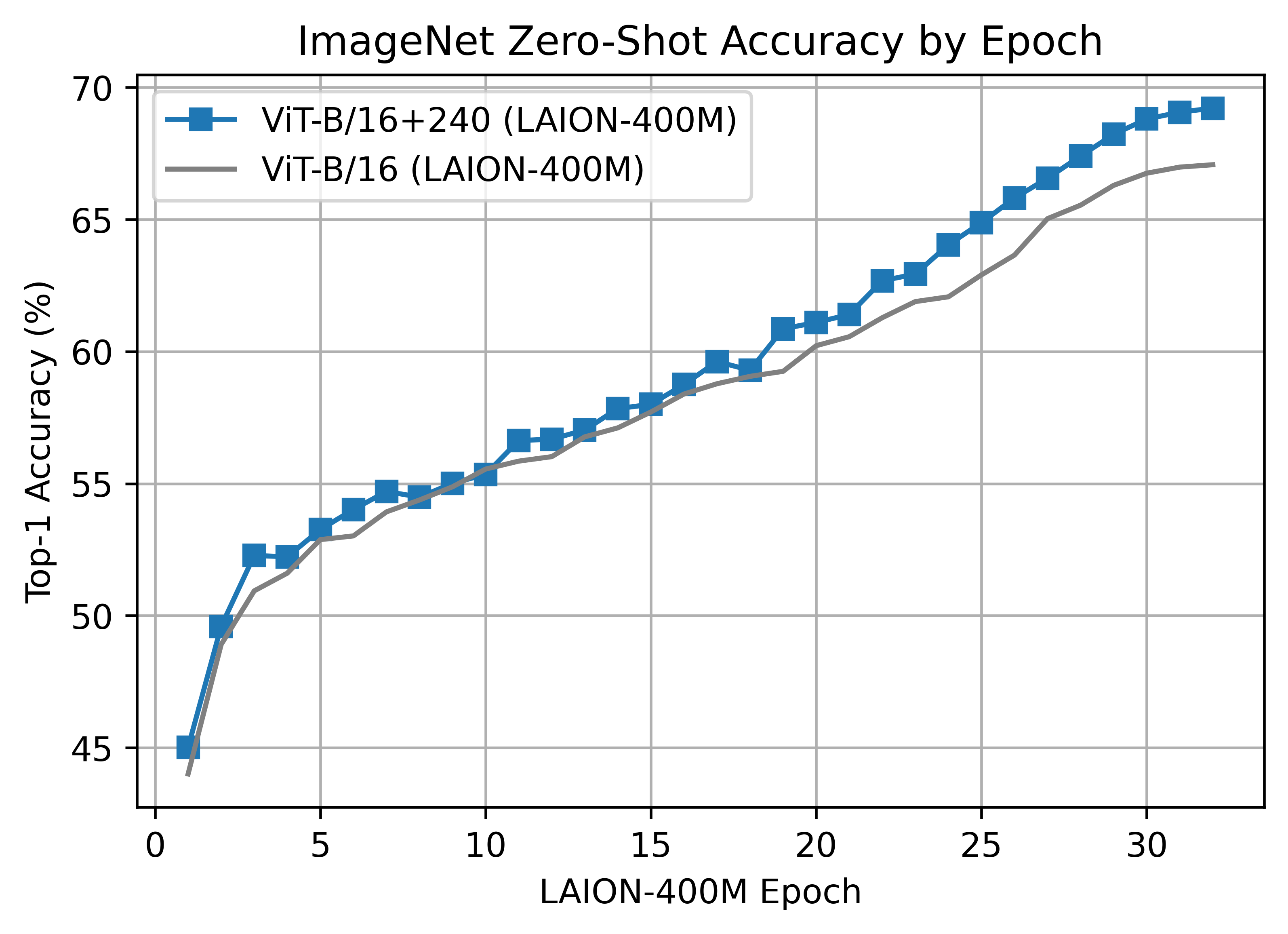 Unlike the B/16 run above, this model was a clean run with no dataset shuffling issues.
ViT-B/16+ was trained with 224 A100 (40 GB) GPUS for ~61 hours, 13620 GPU-hours. Batch size per GPU was 160 for a global batch size of 35840.
#### ViT-L/14 224x224
The L/14 LAION-400M training reached a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot validation score of 72.77.
Unlike the B/16 run above, this model was a clean run with no dataset shuffling issues.
ViT-B/16+ was trained with 224 A100 (40 GB) GPUS for ~61 hours, 13620 GPU-hours. Batch size per GPU was 160 for a global batch size of 35840.
#### ViT-L/14 224x224
The L/14 LAION-400M training reached a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot validation score of 72.77.
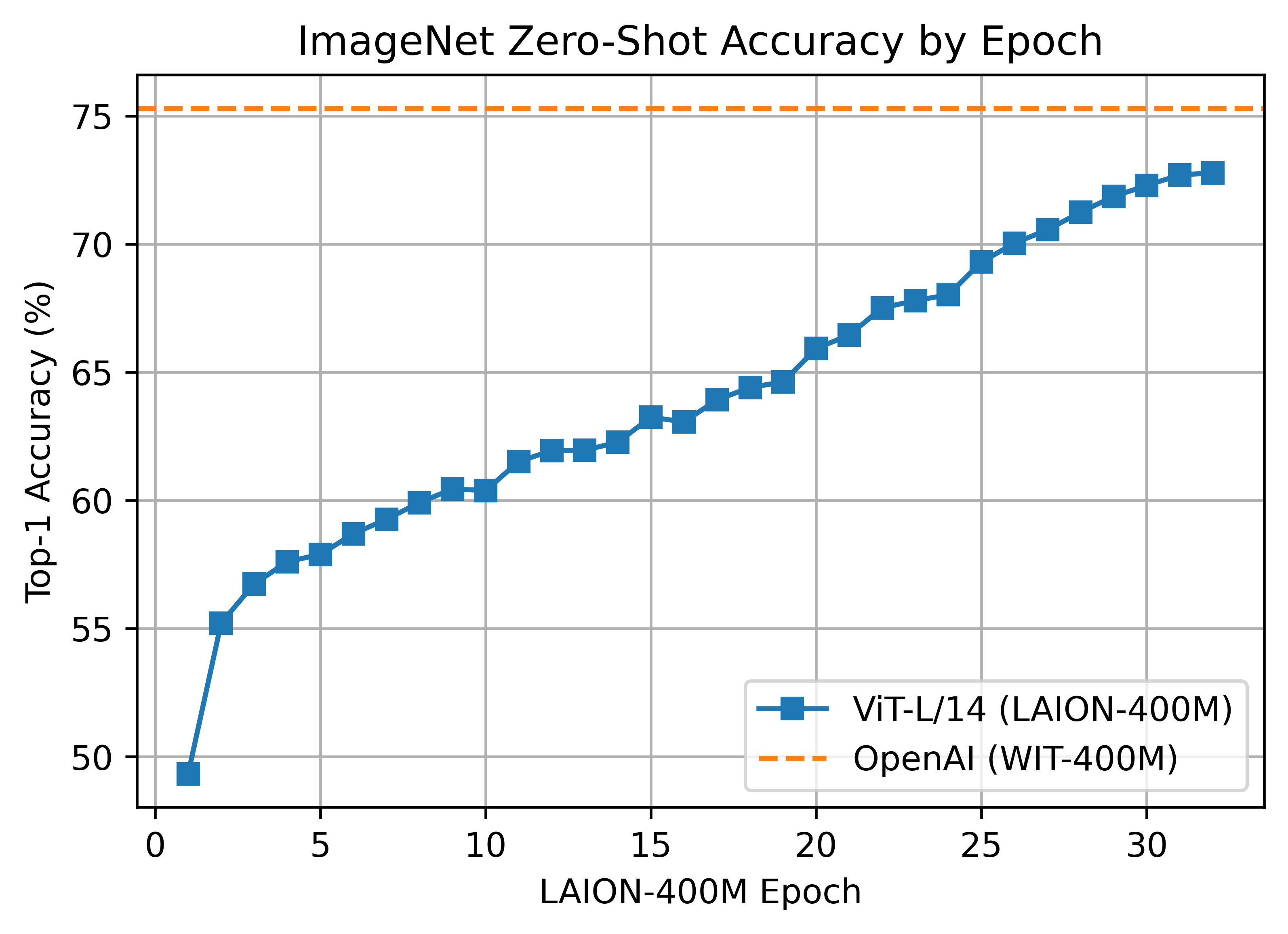 ViT-L/14 was trained with 400 A100 (40 GB) GPUS for ~127 hours, 50800 GPU-hours. Batch size per GPU was 96 for a global batch size of 38400. Grad checkpointing was enabled.
### LAION-2B (en) - https://laion.ai/laion-5b-a-new-era-of-open-large-scale-multi-modal-datasets/
A ~2B sample subset of LAION-5B with english captions (https://huggingface.co/datasets/laion/laion2B-en)
#### ViT-B/32 224x224
A ViT-B/32 trained on LAION-2B, reaching a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot accuracy of 65.62%.
ViT-L/14 was trained with 400 A100 (40 GB) GPUS for ~127 hours, 50800 GPU-hours. Batch size per GPU was 96 for a global batch size of 38400. Grad checkpointing was enabled.
### LAION-2B (en) - https://laion.ai/laion-5b-a-new-era-of-open-large-scale-multi-modal-datasets/
A ~2B sample subset of LAION-5B with english captions (https://huggingface.co/datasets/laion/laion2B-en)
#### ViT-B/32 224x224
A ViT-B/32 trained on LAION-2B, reaching a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot accuracy of 65.62%.
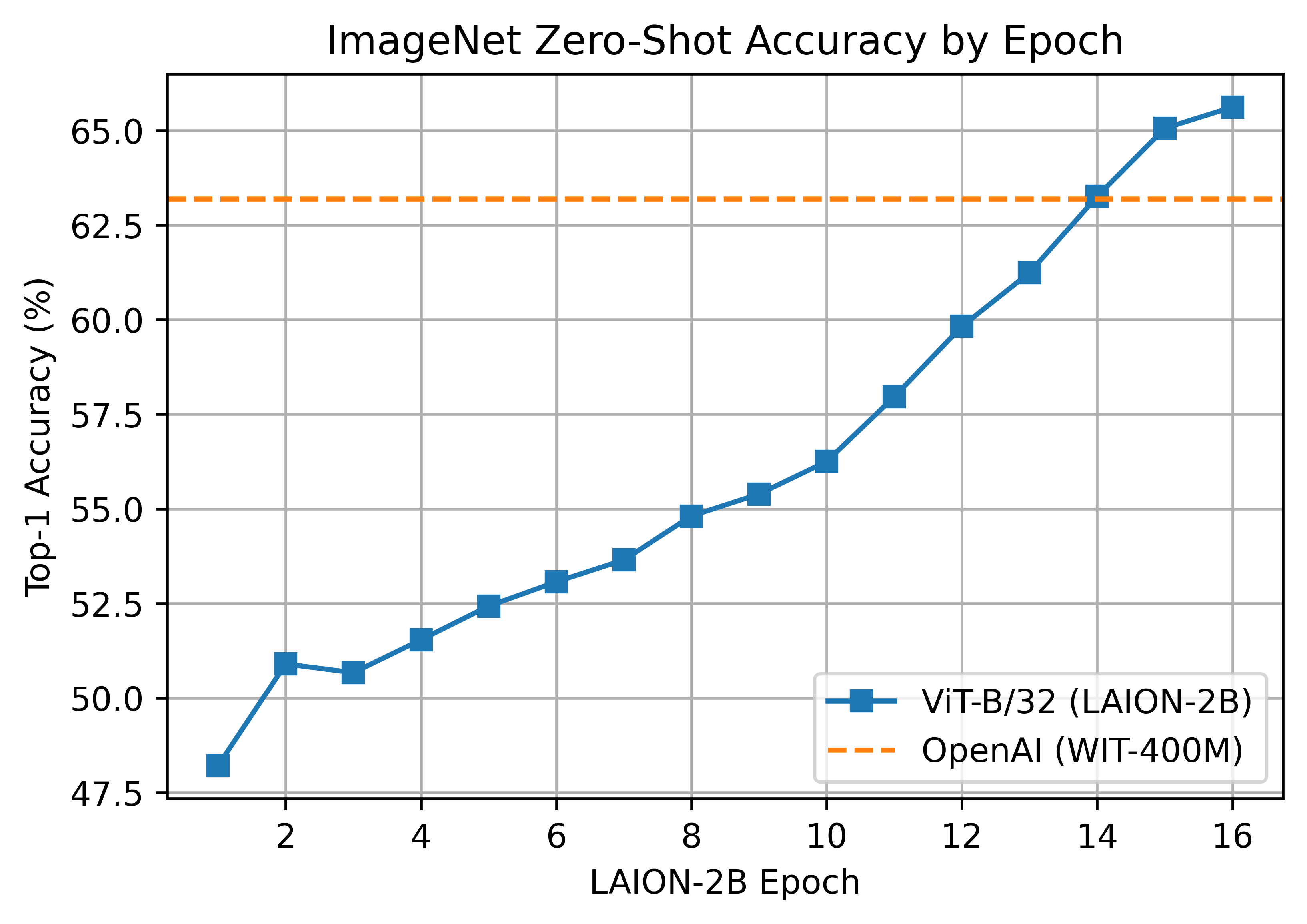 ViT-B/32 was trained with 112 A100 (40 GB) GPUs. The per-GPU batch size was 416 for a global batch size of 46592. Compute generously provided by [stability.ai](https://stability.ai/).
#### YFCC-15M
Below are checkpoints of models trained on YFCC-15M, along with their zero-shot top-1 accuracies on ImageNet and ImageNetV2. These models were trained using 8 GPUs and the same hyperparameters described in the "Sample running code" section, with the exception of `lr=5e-4` and `epochs=32`.
* [ResNet-50](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/download/v0.2-weights/rn50-quickgelu-yfcc15m-455df137.pt) (32.7% / 27.9%)
* [ResNet-101](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/download/v0.2-weights/rn101-quickgelu-yfcc15m-3e04b30e.pt) (34.8% / 30.0%)
#### CC12M - https://github.com/google-research-datasets/conceptual-12m
* [ResNet-50](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/download/v0.2-weights/rn50-quickgelu-cc12m-f000538c.pt) (36.45%)
### Pretrained Model Interface
We offer a simple model interface to instantiate both pre-trained and untrained models.
NOTE: Many existing checkpoints use the QuickGELU activation from the original OpenAI models. This activation is actually less efficient that native torch.nn.GELU in recent versions of PyTorch. The model defaults are now nn.GELU, so one should use model definitions with `-quickgelu` postfix for the OpenCLIP pretrained weights. All OpenAI pretrained weights will always default to QuickGELU. One can also use the non `-quickgelu` model definitions with pretrained weights using QuickGELU but there will be an accuracy drop, for fine-tune that will likely vanish for longer runs.
Future trained models will use nn.GELU.
```python
>>> import open_clip
>>> open_clip.list_pretrained()
[('RN50', 'openai'),
('RN50', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN50', 'cc12m'),
('RN50-quickgelu', 'openai'),
('RN50-quickgelu', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN50-quickgelu', 'cc12m'),
('RN101', 'openai'),
('RN101', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN101-quickgelu', 'openai'),
('RN101-quickgelu', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN50x4', 'openai'),
('RN50x16', 'openai'),
('RN50x64', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-32', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-32', 'laion2b_e16'),
('ViT-B-32', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-32', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-B-16', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-16', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-16', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-B-16-plus-240', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-16-plus-240', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-L-14', 'openai'),
('ViT-L-14-336', 'openai')]
>>> model, train_transform, eval_transform = open_clip.create_model_and_transforms('ViT-B-32', pretrained='laion2b_e16')
```
## Scaling trends
The plot below shows how zero-shot performance of CLIP models varies as we scale the number of samples used for training. Zero-shot performance increases steadily for both ImageNet and [ImageNetV2](https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10811), and is far from saturated at ~15M samples.
ViT-B/32 was trained with 112 A100 (40 GB) GPUs. The per-GPU batch size was 416 for a global batch size of 46592. Compute generously provided by [stability.ai](https://stability.ai/).
#### YFCC-15M
Below are checkpoints of models trained on YFCC-15M, along with their zero-shot top-1 accuracies on ImageNet and ImageNetV2. These models were trained using 8 GPUs and the same hyperparameters described in the "Sample running code" section, with the exception of `lr=5e-4` and `epochs=32`.
* [ResNet-50](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/download/v0.2-weights/rn50-quickgelu-yfcc15m-455df137.pt) (32.7% / 27.9%)
* [ResNet-101](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/download/v0.2-weights/rn101-quickgelu-yfcc15m-3e04b30e.pt) (34.8% / 30.0%)
#### CC12M - https://github.com/google-research-datasets/conceptual-12m
* [ResNet-50](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/download/v0.2-weights/rn50-quickgelu-cc12m-f000538c.pt) (36.45%)
### Pretrained Model Interface
We offer a simple model interface to instantiate both pre-trained and untrained models.
NOTE: Many existing checkpoints use the QuickGELU activation from the original OpenAI models. This activation is actually less efficient that native torch.nn.GELU in recent versions of PyTorch. The model defaults are now nn.GELU, so one should use model definitions with `-quickgelu` postfix for the OpenCLIP pretrained weights. All OpenAI pretrained weights will always default to QuickGELU. One can also use the non `-quickgelu` model definitions with pretrained weights using QuickGELU but there will be an accuracy drop, for fine-tune that will likely vanish for longer runs.
Future trained models will use nn.GELU.
```python
>>> import open_clip
>>> open_clip.list_pretrained()
[('RN50', 'openai'),
('RN50', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN50', 'cc12m'),
('RN50-quickgelu', 'openai'),
('RN50-quickgelu', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN50-quickgelu', 'cc12m'),
('RN101', 'openai'),
('RN101', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN101-quickgelu', 'openai'),
('RN101-quickgelu', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN50x4', 'openai'),
('RN50x16', 'openai'),
('RN50x64', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-32', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-32', 'laion2b_e16'),
('ViT-B-32', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-32', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-B-16', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-16', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-16', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-B-16-plus-240', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-16-plus-240', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-L-14', 'openai'),
('ViT-L-14-336', 'openai')]
>>> model, train_transform, eval_transform = open_clip.create_model_and_transforms('ViT-B-32', pretrained='laion2b_e16')
```
## Scaling trends
The plot below shows how zero-shot performance of CLIP models varies as we scale the number of samples used for training. Zero-shot performance increases steadily for both ImageNet and [ImageNetV2](https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10811), and is far from saturated at ~15M samples.
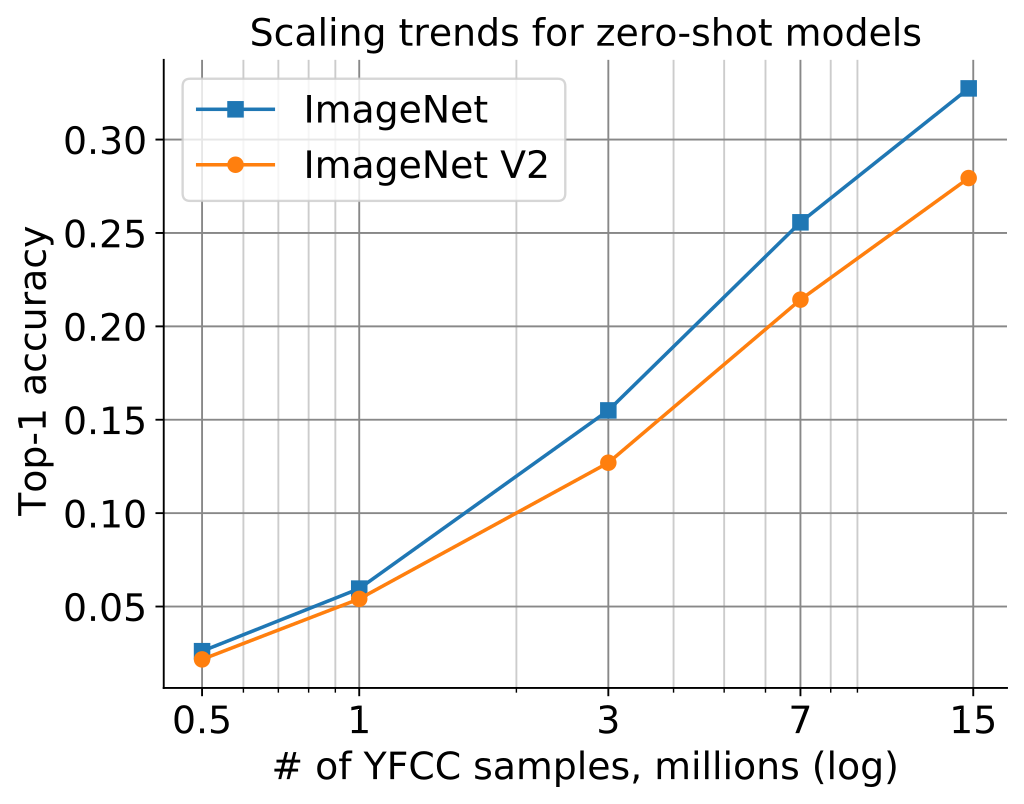 ## Why are low-accuracy CLIP models interesting?
**TL;DR:** CLIP models have high effective robustness, even at small scales.
CLIP models are particularly intriguing because they are more robust to natural distribution shifts (see Section 3.3 in the [CLIP paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020)).
This phenomena is illustrated by the figure below, with ImageNet accuracy on the x-axis
and [ImageNetV2](https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10811) (a reproduction of the ImageNet validation set with distribution shift) accuracy on the y-axis.
Standard training denotes training on the ImageNet train set and the CLIP zero-shot models
are shown as stars.
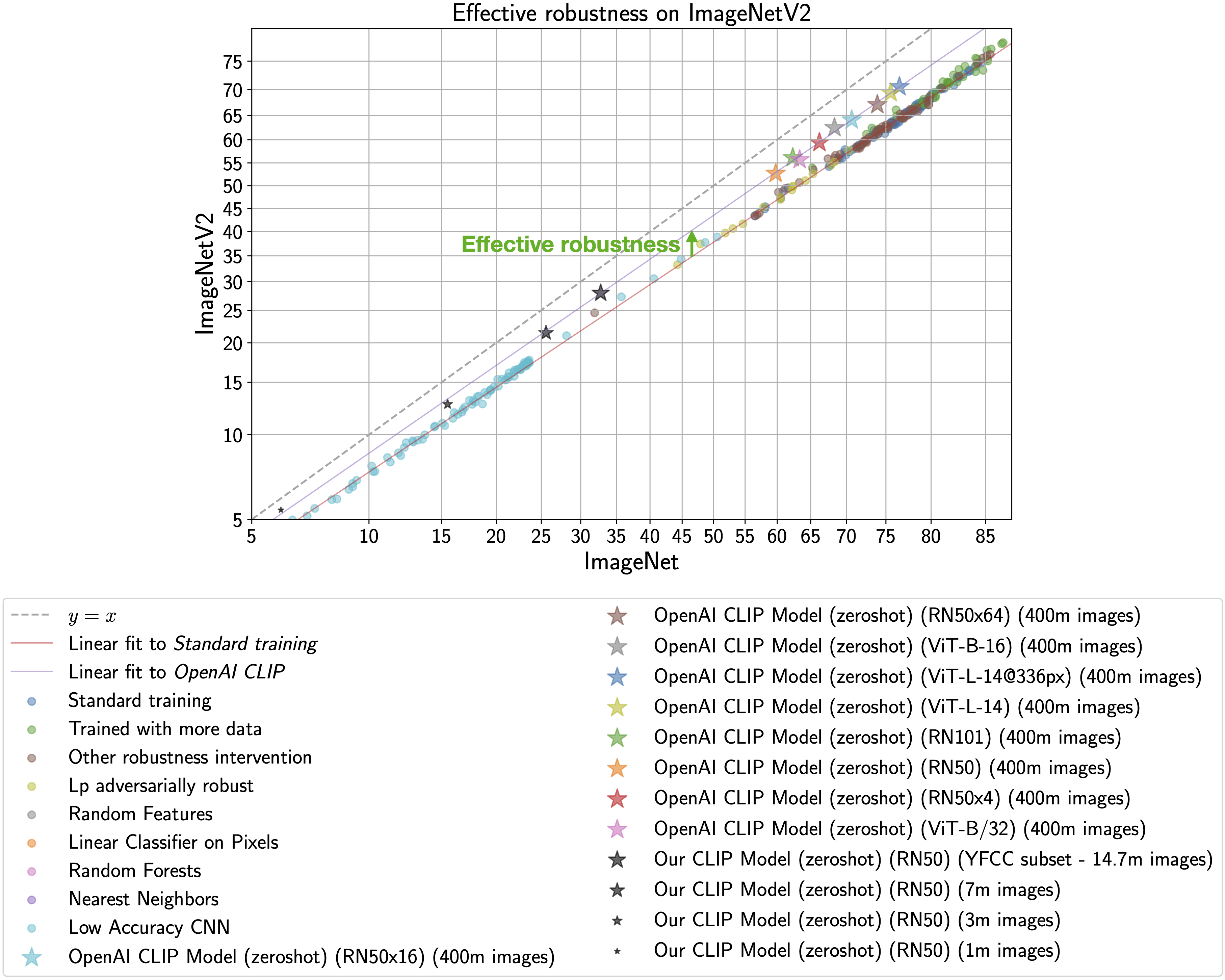
As observed by [Taori et al., 2020](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.00644) and [Miller et al., 2021](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.04649), the in-distribution
and out-of-distribution accuracies of models trained on ImageNet follow a predictable linear trend (the red line in the above plot). *Effective robustness*
quantifies robustness as accuracy beyond this baseline, i.e., how far a model lies above the red line. Ideally a model would not suffer from distribution shift and fall on the y = x line ([trained human labelers are within a percentage point of the y = x line](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v119/shankar20c.html)).
Even though the CLIP models trained with
this codebase achieve much lower accuracy than those trained by OpenAI, our models still lie on the same
trend of improved effective robustness (the purple line). Therefore, we can study what makes
CLIP robust without requiring industrial-scale compute.
For more information on effective robustness, please see:
- [Recht et al., 2019](https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10811).
- [Taori et al., 2020](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.00644).
- [Miller et al., 2021](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.04649).
To know more about the factors that contribute to CLIP's robustness refer to [Fang et al., 2022](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01397).
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the Gauss Centre for Supercomputing e.V. (www.gauss-centre.eu) for funding this part of work by providing computing time through the John von Neumann Institute for Computing (NIC) on the GCS Supercomputer JUWELS Booster at Jülich Supercomputing Centre (JSC).
## The Team
Current development of this repository is led by [Ross Wightman](https://rwightman.com/), [Cade Gordon](http://cadegordon.io/), and [Vaishaal Shankar](http://vaishaal.com/).
The original version of this repository is from a group of researchers at UW, Google, Stanford, Amazon, Columbia, and Berkeley.
[Gabriel Ilharco*](http://gabrielilharco.com/), [Mitchell Wortsman*](https://mitchellnw.github.io/), [Nicholas Carlini](https://nicholas.carlini.com/), [Rohan Taori](https://www.rohantaori.com/), [Achal Dave](http://www.achaldave.com/), [Vaishaal Shankar](http://vaishaal.com/), [John Miller](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~miller_john/), [Hongseok Namkoong](https://hsnamkoong.github.io/), [Hannaneh Hajishirzi](https://homes.cs.washington.edu/~hannaneh/), [Ali Farhadi](https://homes.cs.washington.edu/~ali/), [Ludwig Schmidt](https://people.csail.mit.edu/ludwigs/)
Special thanks to [Jong Wook Kim](https://jongwook.kim/) and [Alec Radford](https://github.com/Newmu) for help with reproducing CLIP!
## Citing
If you found this repository useful, please consider citing:
```bibtex
@software{ilharco_gabriel_2021_5143773,
author = {Ilharco, Gabriel and
Wortsman, Mitchell and
Wightman, Ross and
Gordon, Cade and
Carlini, Nicholas and
Taori, Rohan and
Dave, Achal and
Shankar, Vaishaal and
Namkoong, Hongseok and
Miller, John and
Hajishirzi, Hannaneh and
Farhadi, Ali and
Schmidt, Ludwig},
title = {OpenCLIP},
month = jul,
year = 2021,
note = {If you use this software, please cite it as below.},
publisher = {Zenodo},
version = {0.1},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.5143773},
url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5143773}
}
```
```bibtex
@inproceedings{Radford2021LearningTV,
title={Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision},
author={Alec Radford and Jong Wook Kim and Chris Hallacy and A. Ramesh and Gabriel Goh and Sandhini Agarwal and Girish Sastry and Amanda Askell and Pamela Mishkin and Jack Clark and Gretchen Krueger and Ilya Sutskever},
booktitle={ICML},
year={2021}
}
```
[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/390536799)
## Why are low-accuracy CLIP models interesting?
**TL;DR:** CLIP models have high effective robustness, even at small scales.
CLIP models are particularly intriguing because they are more robust to natural distribution shifts (see Section 3.3 in the [CLIP paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020)).
This phenomena is illustrated by the figure below, with ImageNet accuracy on the x-axis
and [ImageNetV2](https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10811) (a reproduction of the ImageNet validation set with distribution shift) accuracy on the y-axis.
Standard training denotes training on the ImageNet train set and the CLIP zero-shot models
are shown as stars.

As observed by [Taori et al., 2020](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.00644) and [Miller et al., 2021](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.04649), the in-distribution
and out-of-distribution accuracies of models trained on ImageNet follow a predictable linear trend (the red line in the above plot). *Effective robustness*
quantifies robustness as accuracy beyond this baseline, i.e., how far a model lies above the red line. Ideally a model would not suffer from distribution shift and fall on the y = x line ([trained human labelers are within a percentage point of the y = x line](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v119/shankar20c.html)).
Even though the CLIP models trained with
this codebase achieve much lower accuracy than those trained by OpenAI, our models still lie on the same
trend of improved effective robustness (the purple line). Therefore, we can study what makes
CLIP robust without requiring industrial-scale compute.
For more information on effective robustness, please see:
- [Recht et al., 2019](https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10811).
- [Taori et al., 2020](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.00644).
- [Miller et al., 2021](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.04649).
To know more about the factors that contribute to CLIP's robustness refer to [Fang et al., 2022](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01397).
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the Gauss Centre for Supercomputing e.V. (www.gauss-centre.eu) for funding this part of work by providing computing time through the John von Neumann Institute for Computing (NIC) on the GCS Supercomputer JUWELS Booster at Jülich Supercomputing Centre (JSC).
## The Team
Current development of this repository is led by [Ross Wightman](https://rwightman.com/), [Cade Gordon](http://cadegordon.io/), and [Vaishaal Shankar](http://vaishaal.com/).
The original version of this repository is from a group of researchers at UW, Google, Stanford, Amazon, Columbia, and Berkeley.
[Gabriel Ilharco*](http://gabrielilharco.com/), [Mitchell Wortsman*](https://mitchellnw.github.io/), [Nicholas Carlini](https://nicholas.carlini.com/), [Rohan Taori](https://www.rohantaori.com/), [Achal Dave](http://www.achaldave.com/), [Vaishaal Shankar](http://vaishaal.com/), [John Miller](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~miller_john/), [Hongseok Namkoong](https://hsnamkoong.github.io/), [Hannaneh Hajishirzi](https://homes.cs.washington.edu/~hannaneh/), [Ali Farhadi](https://homes.cs.washington.edu/~ali/), [Ludwig Schmidt](https://people.csail.mit.edu/ludwigs/)
Special thanks to [Jong Wook Kim](https://jongwook.kim/) and [Alec Radford](https://github.com/Newmu) for help with reproducing CLIP!
## Citing
If you found this repository useful, please consider citing:
```bibtex
@software{ilharco_gabriel_2021_5143773,
author = {Ilharco, Gabriel and
Wortsman, Mitchell and
Wightman, Ross and
Gordon, Cade and
Carlini, Nicholas and
Taori, Rohan and
Dave, Achal and
Shankar, Vaishaal and
Namkoong, Hongseok and
Miller, John and
Hajishirzi, Hannaneh and
Farhadi, Ali and
Schmidt, Ludwig},
title = {OpenCLIP},
month = jul,
year = 2021,
note = {If you use this software, please cite it as below.},
publisher = {Zenodo},
version = {0.1},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.5143773},
url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5143773}
}
```
```bibtex
@inproceedings{Radford2021LearningTV,
title={Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision},
author={Alec Radford and Jong Wook Kim and Chris Hallacy and A. Ramesh and Gabriel Goh and Sandhini Agarwal and Girish Sastry and Amanda Askell and Pamela Mishkin and Jack Clark and Gretchen Krueger and Ilya Sutskever},
booktitle={ICML},
year={2021}
}
```
[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/390536799)
 __Zero-shot comparison (courtesy of Andreas Fürst)__
__Zero-shot comparison (courtesy of Andreas Fürst)__
 ViT-B/32 was trained with 128 A100 (40 GB) GPUs for ~36 hours, 4600 GPU-hours. The per-GPU batch size was 256 for a global batch size of 32768. 256 is much lower than it could have been (~320-384) due to being sized initially before moving to 'local' contrastive loss.
#### ViT-B/16 224x224
The B/16 LAION400M training reached a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot validation score of 67.07.
ViT-B/32 was trained with 128 A100 (40 GB) GPUs for ~36 hours, 4600 GPU-hours. The per-GPU batch size was 256 for a global batch size of 32768. 256 is much lower than it could have been (~320-384) due to being sized initially before moving to 'local' contrastive loss.
#### ViT-B/16 224x224
The B/16 LAION400M training reached a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot validation score of 67.07.
 This was the first major train session using the updated webdataset 0.2.x code. A bug was found that prevented shards from being shuffled properly between nodes/workers each epoch. This was fixed part way through training (epoch 26) but likely had an impact.
ViT-B/16 was trained with 176 A100 (40 GB) GPUS for ~61 hours, 10700 GPU-hours. Batch size per GPU was 192 for a global batch size of 33792.
#### ViT-B/16+ 240x240
The B/16+ 240x240 LAION400M training reached a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot validation score of 69.21.
This model is the same depth as the B/16, but increases the
* vision width from 768 -> 896
* text width from 512 -> 640
* the resolution 224x224 -> 240x240 (196 -> 225 tokens)
This was the first major train session using the updated webdataset 0.2.x code. A bug was found that prevented shards from being shuffled properly between nodes/workers each epoch. This was fixed part way through training (epoch 26) but likely had an impact.
ViT-B/16 was trained with 176 A100 (40 GB) GPUS for ~61 hours, 10700 GPU-hours. Batch size per GPU was 192 for a global batch size of 33792.
#### ViT-B/16+ 240x240
The B/16+ 240x240 LAION400M training reached a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot validation score of 69.21.
This model is the same depth as the B/16, but increases the
* vision width from 768 -> 896
* text width from 512 -> 640
* the resolution 224x224 -> 240x240 (196 -> 225 tokens)
 Unlike the B/16 run above, this model was a clean run with no dataset shuffling issues.
ViT-B/16+ was trained with 224 A100 (40 GB) GPUS for ~61 hours, 13620 GPU-hours. Batch size per GPU was 160 for a global batch size of 35840.
#### ViT-L/14 224x224
The L/14 LAION-400M training reached a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot validation score of 72.77.
Unlike the B/16 run above, this model was a clean run with no dataset shuffling issues.
ViT-B/16+ was trained with 224 A100 (40 GB) GPUS for ~61 hours, 13620 GPU-hours. Batch size per GPU was 160 for a global batch size of 35840.
#### ViT-L/14 224x224
The L/14 LAION-400M training reached a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot validation score of 72.77.
 ViT-L/14 was trained with 400 A100 (40 GB) GPUS for ~127 hours, 50800 GPU-hours. Batch size per GPU was 96 for a global batch size of 38400. Grad checkpointing was enabled.
### LAION-2B (en) - https://laion.ai/laion-5b-a-new-era-of-open-large-scale-multi-modal-datasets/
A ~2B sample subset of LAION-5B with english captions (https://huggingface.co/datasets/laion/laion2B-en)
#### ViT-B/32 224x224
A ViT-B/32 trained on LAION-2B, reaching a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot accuracy of 65.62%.
ViT-L/14 was trained with 400 A100 (40 GB) GPUS for ~127 hours, 50800 GPU-hours. Batch size per GPU was 96 for a global batch size of 38400. Grad checkpointing was enabled.
### LAION-2B (en) - https://laion.ai/laion-5b-a-new-era-of-open-large-scale-multi-modal-datasets/
A ~2B sample subset of LAION-5B with english captions (https://huggingface.co/datasets/laion/laion2B-en)
#### ViT-B/32 224x224
A ViT-B/32 trained on LAION-2B, reaching a top-1 ImageNet-1k zero-shot accuracy of 65.62%.
 ViT-B/32 was trained with 112 A100 (40 GB) GPUs. The per-GPU batch size was 416 for a global batch size of 46592. Compute generously provided by [stability.ai](https://stability.ai/).
#### YFCC-15M
Below are checkpoints of models trained on YFCC-15M, along with their zero-shot top-1 accuracies on ImageNet and ImageNetV2. These models were trained using 8 GPUs and the same hyperparameters described in the "Sample running code" section, with the exception of `lr=5e-4` and `epochs=32`.
* [ResNet-50](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/download/v0.2-weights/rn50-quickgelu-yfcc15m-455df137.pt) (32.7% / 27.9%)
* [ResNet-101](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/download/v0.2-weights/rn101-quickgelu-yfcc15m-3e04b30e.pt) (34.8% / 30.0%)
#### CC12M - https://github.com/google-research-datasets/conceptual-12m
* [ResNet-50](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/download/v0.2-weights/rn50-quickgelu-cc12m-f000538c.pt) (36.45%)
### Pretrained Model Interface
We offer a simple model interface to instantiate both pre-trained and untrained models.
NOTE: Many existing checkpoints use the QuickGELU activation from the original OpenAI models. This activation is actually less efficient that native torch.nn.GELU in recent versions of PyTorch. The model defaults are now nn.GELU, so one should use model definitions with `-quickgelu` postfix for the OpenCLIP pretrained weights. All OpenAI pretrained weights will always default to QuickGELU. One can also use the non `-quickgelu` model definitions with pretrained weights using QuickGELU but there will be an accuracy drop, for fine-tune that will likely vanish for longer runs.
Future trained models will use nn.GELU.
```python
>>> import open_clip
>>> open_clip.list_pretrained()
[('RN50', 'openai'),
('RN50', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN50', 'cc12m'),
('RN50-quickgelu', 'openai'),
('RN50-quickgelu', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN50-quickgelu', 'cc12m'),
('RN101', 'openai'),
('RN101', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN101-quickgelu', 'openai'),
('RN101-quickgelu', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN50x4', 'openai'),
('RN50x16', 'openai'),
('RN50x64', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-32', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-32', 'laion2b_e16'),
('ViT-B-32', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-32', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-B-16', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-16', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-16', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-B-16-plus-240', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-16-plus-240', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-L-14', 'openai'),
('ViT-L-14-336', 'openai')]
>>> model, train_transform, eval_transform = open_clip.create_model_and_transforms('ViT-B-32', pretrained='laion2b_e16')
```
## Scaling trends
The plot below shows how zero-shot performance of CLIP models varies as we scale the number of samples used for training. Zero-shot performance increases steadily for both ImageNet and [ImageNetV2](https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10811), and is far from saturated at ~15M samples.
ViT-B/32 was trained with 112 A100 (40 GB) GPUs. The per-GPU batch size was 416 for a global batch size of 46592. Compute generously provided by [stability.ai](https://stability.ai/).
#### YFCC-15M
Below are checkpoints of models trained on YFCC-15M, along with their zero-shot top-1 accuracies on ImageNet and ImageNetV2. These models were trained using 8 GPUs and the same hyperparameters described in the "Sample running code" section, with the exception of `lr=5e-4` and `epochs=32`.
* [ResNet-50](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/download/v0.2-weights/rn50-quickgelu-yfcc15m-455df137.pt) (32.7% / 27.9%)
* [ResNet-101](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/download/v0.2-weights/rn101-quickgelu-yfcc15m-3e04b30e.pt) (34.8% / 30.0%)
#### CC12M - https://github.com/google-research-datasets/conceptual-12m
* [ResNet-50](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/releases/download/v0.2-weights/rn50-quickgelu-cc12m-f000538c.pt) (36.45%)
### Pretrained Model Interface
We offer a simple model interface to instantiate both pre-trained and untrained models.
NOTE: Many existing checkpoints use the QuickGELU activation from the original OpenAI models. This activation is actually less efficient that native torch.nn.GELU in recent versions of PyTorch. The model defaults are now nn.GELU, so one should use model definitions with `-quickgelu` postfix for the OpenCLIP pretrained weights. All OpenAI pretrained weights will always default to QuickGELU. One can also use the non `-quickgelu` model definitions with pretrained weights using QuickGELU but there will be an accuracy drop, for fine-tune that will likely vanish for longer runs.
Future trained models will use nn.GELU.
```python
>>> import open_clip
>>> open_clip.list_pretrained()
[('RN50', 'openai'),
('RN50', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN50', 'cc12m'),
('RN50-quickgelu', 'openai'),
('RN50-quickgelu', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN50-quickgelu', 'cc12m'),
('RN101', 'openai'),
('RN101', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN101-quickgelu', 'openai'),
('RN101-quickgelu', 'yfcc15m'),
('RN50x4', 'openai'),
('RN50x16', 'openai'),
('RN50x64', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-32', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-32', 'laion2b_e16'),
('ViT-B-32', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-32', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-32-quickgelu', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-B-16', 'openai'),
('ViT-B-16', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-16', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-B-16-plus-240', 'laion400m_e31'),
('ViT-B-16-plus-240', 'laion400m_e32'),
('ViT-L-14', 'openai'),
('ViT-L-14-336', 'openai')]
>>> model, train_transform, eval_transform = open_clip.create_model_and_transforms('ViT-B-32', pretrained='laion2b_e16')
```
## Scaling trends
The plot below shows how zero-shot performance of CLIP models varies as we scale the number of samples used for training. Zero-shot performance increases steadily for both ImageNet and [ImageNetV2](https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10811), and is far from saturated at ~15M samples.
 ## Why are low-accuracy CLIP models interesting?
**TL;DR:** CLIP models have high effective robustness, even at small scales.
CLIP models are particularly intriguing because they are more robust to natural distribution shifts (see Section 3.3 in the [CLIP paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020)).
This phenomena is illustrated by the figure below, with ImageNet accuracy on the x-axis
and [ImageNetV2](https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10811) (a reproduction of the ImageNet validation set with distribution shift) accuracy on the y-axis.
Standard training denotes training on the ImageNet train set and the CLIP zero-shot models
are shown as stars.

As observed by [Taori et al., 2020](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.00644) and [Miller et al., 2021](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.04649), the in-distribution
and out-of-distribution accuracies of models trained on ImageNet follow a predictable linear trend (the red line in the above plot). *Effective robustness*
quantifies robustness as accuracy beyond this baseline, i.e., how far a model lies above the red line. Ideally a model would not suffer from distribution shift and fall on the y = x line ([trained human labelers are within a percentage point of the y = x line](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v119/shankar20c.html)).
Even though the CLIP models trained with
this codebase achieve much lower accuracy than those trained by OpenAI, our models still lie on the same
trend of improved effective robustness (the purple line). Therefore, we can study what makes
CLIP robust without requiring industrial-scale compute.
For more information on effective robustness, please see:
- [Recht et al., 2019](https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10811).
- [Taori et al., 2020](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.00644).
- [Miller et al., 2021](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.04649).
To know more about the factors that contribute to CLIP's robustness refer to [Fang et al., 2022](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01397).
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the Gauss Centre for Supercomputing e.V. (www.gauss-centre.eu) for funding this part of work by providing computing time through the John von Neumann Institute for Computing (NIC) on the GCS Supercomputer JUWELS Booster at Jülich Supercomputing Centre (JSC).
## The Team
Current development of this repository is led by [Ross Wightman](https://rwightman.com/), [Cade Gordon](http://cadegordon.io/), and [Vaishaal Shankar](http://vaishaal.com/).
The original version of this repository is from a group of researchers at UW, Google, Stanford, Amazon, Columbia, and Berkeley.
[Gabriel Ilharco*](http://gabrielilharco.com/), [Mitchell Wortsman*](https://mitchellnw.github.io/), [Nicholas Carlini](https://nicholas.carlini.com/), [Rohan Taori](https://www.rohantaori.com/), [Achal Dave](http://www.achaldave.com/), [Vaishaal Shankar](http://vaishaal.com/), [John Miller](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~miller_john/), [Hongseok Namkoong](https://hsnamkoong.github.io/), [Hannaneh Hajishirzi](https://homes.cs.washington.edu/~hannaneh/), [Ali Farhadi](https://homes.cs.washington.edu/~ali/), [Ludwig Schmidt](https://people.csail.mit.edu/ludwigs/)
Special thanks to [Jong Wook Kim](https://jongwook.kim/) and [Alec Radford](https://github.com/Newmu) for help with reproducing CLIP!
## Citing
If you found this repository useful, please consider citing:
```bibtex
@software{ilharco_gabriel_2021_5143773,
author = {Ilharco, Gabriel and
Wortsman, Mitchell and
Wightman, Ross and
Gordon, Cade and
Carlini, Nicholas and
Taori, Rohan and
Dave, Achal and
Shankar, Vaishaal and
Namkoong, Hongseok and
Miller, John and
Hajishirzi, Hannaneh and
Farhadi, Ali and
Schmidt, Ludwig},
title = {OpenCLIP},
month = jul,
year = 2021,
note = {If you use this software, please cite it as below.},
publisher = {Zenodo},
version = {0.1},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.5143773},
url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5143773}
}
```
```bibtex
@inproceedings{Radford2021LearningTV,
title={Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision},
author={Alec Radford and Jong Wook Kim and Chris Hallacy and A. Ramesh and Gabriel Goh and Sandhini Agarwal and Girish Sastry and Amanda Askell and Pamela Mishkin and Jack Clark and Gretchen Krueger and Ilya Sutskever},
booktitle={ICML},
year={2021}
}
```
[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/390536799)
## Why are low-accuracy CLIP models interesting?
**TL;DR:** CLIP models have high effective robustness, even at small scales.
CLIP models are particularly intriguing because they are more robust to natural distribution shifts (see Section 3.3 in the [CLIP paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020)).
This phenomena is illustrated by the figure below, with ImageNet accuracy on the x-axis
and [ImageNetV2](https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10811) (a reproduction of the ImageNet validation set with distribution shift) accuracy on the y-axis.
Standard training denotes training on the ImageNet train set and the CLIP zero-shot models
are shown as stars.

As observed by [Taori et al., 2020](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.00644) and [Miller et al., 2021](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.04649), the in-distribution
and out-of-distribution accuracies of models trained on ImageNet follow a predictable linear trend (the red line in the above plot). *Effective robustness*
quantifies robustness as accuracy beyond this baseline, i.e., how far a model lies above the red line. Ideally a model would not suffer from distribution shift and fall on the y = x line ([trained human labelers are within a percentage point of the y = x line](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v119/shankar20c.html)).
Even though the CLIP models trained with
this codebase achieve much lower accuracy than those trained by OpenAI, our models still lie on the same
trend of improved effective robustness (the purple line). Therefore, we can study what makes
CLIP robust without requiring industrial-scale compute.
For more information on effective robustness, please see:
- [Recht et al., 2019](https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10811).
- [Taori et al., 2020](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.00644).
- [Miller et al., 2021](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.04649).
To know more about the factors that contribute to CLIP's robustness refer to [Fang et al., 2022](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01397).
## Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the Gauss Centre for Supercomputing e.V. (www.gauss-centre.eu) for funding this part of work by providing computing time through the John von Neumann Institute for Computing (NIC) on the GCS Supercomputer JUWELS Booster at Jülich Supercomputing Centre (JSC).
## The Team
Current development of this repository is led by [Ross Wightman](https://rwightman.com/), [Cade Gordon](http://cadegordon.io/), and [Vaishaal Shankar](http://vaishaal.com/).
The original version of this repository is from a group of researchers at UW, Google, Stanford, Amazon, Columbia, and Berkeley.
[Gabriel Ilharco*](http://gabrielilharco.com/), [Mitchell Wortsman*](https://mitchellnw.github.io/), [Nicholas Carlini](https://nicholas.carlini.com/), [Rohan Taori](https://www.rohantaori.com/), [Achal Dave](http://www.achaldave.com/), [Vaishaal Shankar](http://vaishaal.com/), [John Miller](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~miller_john/), [Hongseok Namkoong](https://hsnamkoong.github.io/), [Hannaneh Hajishirzi](https://homes.cs.washington.edu/~hannaneh/), [Ali Farhadi](https://homes.cs.washington.edu/~ali/), [Ludwig Schmidt](https://people.csail.mit.edu/ludwigs/)
Special thanks to [Jong Wook Kim](https://jongwook.kim/) and [Alec Radford](https://github.com/Newmu) for help with reproducing CLIP!
## Citing
If you found this repository useful, please consider citing:
```bibtex
@software{ilharco_gabriel_2021_5143773,
author = {Ilharco, Gabriel and
Wortsman, Mitchell and
Wightman, Ross and
Gordon, Cade and
Carlini, Nicholas and
Taori, Rohan and
Dave, Achal and
Shankar, Vaishaal and
Namkoong, Hongseok and
Miller, John and
Hajishirzi, Hannaneh and
Farhadi, Ali and
Schmidt, Ludwig},
title = {OpenCLIP},
month = jul,
year = 2021,
note = {If you use this software, please cite it as below.},
publisher = {Zenodo},
version = {0.1},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.5143773},
url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5143773}
}
```
```bibtex
@inproceedings{Radford2021LearningTV,
title={Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision},
author={Alec Radford and Jong Wook Kim and Chris Hallacy and A. Ramesh and Gabriel Goh and Sandhini Agarwal and Girish Sastry and Amanda Askell and Pamela Mishkin and Jack Clark and Gretchen Krueger and Ilya Sutskever},
booktitle={ICML},
year={2021}
}
```
[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/390536799)