Spaces:
Sleeping
Sleeping
Commit
·
4a832b8
1
Parent(s):
798f3fb
Add additional content
Browse files- Cross-over.png +0 -0
- Decision Tree Algorithm.webp +0 -0
- GA_KKPM.ipynb +0 -0
- Genetic_Algorithm.py +70 -0
- Gini method.webp +0 -0
- Heart_Disease.ipynb +0 -0
- Mutation.png +0 -0
- Terminology for Genetic Algorithm.png +0 -0
- The Decision Tree Algorithm.png +0 -0
- The Gini Index.webp +0 -0
- Working of Genetic Algorithm.png +0 -0
- pages/1_Heart_Disease.py +42 -0
- pages/2_Dataset_Information.py +21 -0
- pages/3_Variables_Table.py +31 -0
- pages/4_Decision_Tree_Classification.py +68 -0
- pages/5_Heart_Disease_Prediction.py +57 -0
- pages/__pycache__/about.cpython-311.pyc +0 -0
- pages/__pycache__/genetic_algorithm.cpython-311.pyc +0 -0
- smaller gini index.webp +0 -0
Cross-over.png
ADDED

|
Decision Tree Algorithm.webp
ADDED
|
GA_KKPM.ipynb
CHANGED
|
The diff for this file is too large to render.
See raw diff
|
|
|
Genetic_Algorithm.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
import streamlit as st
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
def main():
|
| 4 |
+
st.set_page_config(page_title="Genetic Algorithm for Feature Selection", layout="wide")
|
| 5 |
+
|
| 6 |
+
st.title("Genetic Algorithm for Feature Selection")
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
# Introduction and Description
|
| 9 |
+
st.header("Genetic Algorithm")
|
| 10 |
+
st.markdown("""
|
| 11 |
+
<div style='text-align: justify;'>
|
| 12 |
+
The Genetic Algorithm (GA) is an evolutionary algorithm (EA) inspired by Charles Darwin’s theory of natural selection which espouses Survival of the fittest. As per the natural selection theory, the fittest individuals are selected to produce offsprings. The fittest parents' characteristics are then passed on to their offsprings using cross-over and mutation to ensure better chances of survival. Genetic algorithms are randomized search algorithms that generate high-quality optimization solutions by imitating the biologically inspired natural selection process such as selection, cross-over, and mutation.
|
| 13 |
+
</div>
|
| 14 |
+
""", unsafe_allow_html=True)
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
# Terminology
|
| 17 |
+
st.header("Terminology for Genetic Algorithm")
|
| 18 |
+
st.image("Terminology for Genetic Algorithm.png")
|
| 19 |
+
st.markdown("""
|
| 20 |
+
- **Population**: A set of possible solutions for the stochastic search process to begin. GA iterates over multiple generations till it finds an acceptable and optimized solution. The first generation is randomly generated.
|
| 21 |
+
- **Chromosome**: Represents one candidate solution present in the generation or population, also referred to as a Genotype. A chromosome is composed of Genes that contain the value for the optimal variables.
|
| 22 |
+
- **Phenotype**: The decoded parameter list for the genotype that is processed by the Genetic Algorithm. Mapping is applied to the genotype to convert to a phenotype.
|
| 23 |
+
- **Fitness Function**: Or the objective function evaluates the individual solution or phenotypes for every generation to identify the fittest members.
|
| 24 |
+
""", unsafe_allow_html=True)
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
# Genetic Operators
|
| 27 |
+
st.header("Different Genetic Operators")
|
| 28 |
+
st.markdown("""
|
| 29 |
+
- **Selection**: The process of selecting the fittest solution from a population. The fittest solutions act as parents for the next generation. Selection can be performed using Roulette Wheel Selection or Ranked Selection based on the fitness value.
|
| 30 |
+
""", unsafe_allow_html=True)
|
| 31 |
+
st.markdown("""
|
| 32 |
+
- **Cross-over or Recombination**: Happens when genes from the two fittest parents are randomly exchanged to form a new genotype or solution. Cross over can be a One-point cross over or Multi-Point Cross over based on the parent's segments of genes exchanged.
|
| 33 |
+
""", unsafe_allow_html=True)
|
| 34 |
+
st.image("Cross-over.png")
|
| 35 |
+
|
| 36 |
+
st.markdown("""
|
| 37 |
+
- **Mutation**: After a new population is created through selection and crossover, it is randomly modified through mutation to promote diversity in the population to find better and optimized solutions.
|
| 38 |
+
""", unsafe_allow_html=True)
|
| 39 |
+
st.image("Mutation.png")
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
# Usage in AI
|
| 42 |
+
st.header("Usage of Genetic Algorithm in Artificial Intelligence")
|
| 43 |
+
st.markdown("""
|
| 44 |
+
A Genetic Algorithm is used for Search and Optimization using an iterative process to arrive at the best solution out of multiple solutions. For instance:
|
| 45 |
+
1. Finding an appropriate set of hyperparameters for a deep learning model to increase its performance.
|
| 46 |
+
2. Determining the best amount of features to include in a machine learning model for predicting the target variable.
|
| 47 |
+
""", unsafe_allow_html=True)
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
# Working of Genetic Algorithm
|
| 50 |
+
st.header("Working of Genetic Algorithm")
|
| 51 |
+
st.image("Working of Genetic Algorithm.png")
|
| 52 |
+
|
| 53 |
+
# Implementation
|
| 54 |
+
st.header("Implementation of Genetic Algorithm for Feature Selection")
|
| 55 |
+
st.markdown("""
|
| 56 |
+
The implementation involves several steps:
|
| 57 |
+
1. Initializing a random population.
|
| 58 |
+
2. Running the population through a fitness function to return the best parents (highest accuracy).
|
| 59 |
+
3. Selection from these best parents will occur depending on the n-parent parameter.
|
| 60 |
+
4. These parents are then put through the crossover and mutation functions respectively.
|
| 61 |
+
5. A new generation is created by selecting the fittest parents from the previous generation and applying cross-over and mutation.
|
| 62 |
+
6. This process is repeated for a specified number of generations.
|
| 63 |
+
""", unsafe_allow_html=True)
|
| 64 |
+
|
| 65 |
+
# Add a footer
|
| 66 |
+
st.markdown("---")
|
| 67 |
+
st.write("Made with ❤️ by Viga, Hanum, & Robit")
|
| 68 |
+
|
| 69 |
+
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 70 |
+
main()
|
Gini method.webp
ADDED

|
Heart_Disease.ipynb
ADDED
|
The diff for this file is too large to render.
See raw diff
|
|
|
Mutation.png
ADDED

|
Terminology for Genetic Algorithm.png
ADDED

|
The Decision Tree Algorithm.png
ADDED

|
The Gini Index.webp
ADDED
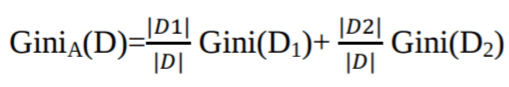
|
Working of Genetic Algorithm.png
ADDED

|
pages/1_Heart_Disease.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
import streamlit as st
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
def main():
|
| 4 |
+
st.set_page_config(page_title="Heart Disease")
|
| 5 |
+
|
| 6 |
+
# Page title and subtitle with styling
|
| 7 |
+
st.title("Heart Disease")
|
| 8 |
+
st.markdown("*Donated on 6/30/1988*")
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
# Load and display an image
|
| 11 |
+
st.image("heart_image.jpg")
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
# Dataset information
|
| 14 |
+
st.header("Dataset Information")
|
| 15 |
+
st.write("This dataset contains information from 4 databases: Cleveland, Hungary, Switzerland, and the VA Long Beach")
|
| 16 |
+
|
| 17 |
+
# Dataset characteristics
|
| 18 |
+
st.header("Dataset Characteristics")
|
| 19 |
+
st.write("This dataset is multivariate")
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
# Subject area
|
| 22 |
+
st.header("Subject Area")
|
| 23 |
+
st.write("This dataset falls under the category of Health and Medicine")
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
# Associated tasks
|
| 26 |
+
st.header("Associated Tasks")
|
| 27 |
+
st.write("This dataset is commonly used for Classification tasks")
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
# Feature types
|
| 30 |
+
st.header("Feature Type")
|
| 31 |
+
st.write("This dataset contains a mix of Categorical, Integer, and Real features")
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
# Instances and Features
|
| 34 |
+
st.write("**Number of Instances:** 303")
|
| 35 |
+
st.write("**Number of Features:** 13")
|
| 36 |
+
|
| 37 |
+
# Add a footer
|
| 38 |
+
st.markdown("---")
|
| 39 |
+
st.write("Made with ❤️ by Viga, Hanum, & Robit")
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 42 |
+
main()
|
pages/2_Dataset_Information.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
import streamlit as st
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
def run():
|
| 4 |
+
st.set_page_config(page_title="Dataset Information")
|
| 5 |
+
|
| 6 |
+
st.title("Dataset Information")
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
# Additional Information
|
| 9 |
+
st.header("Additional Information")
|
| 10 |
+
st.markdown('<div style="text-align: justify;">This database contains 76 attributes, but all published experiments refer to using a subset of 14 of them. In particular, the Cleveland database is the only one that has been used by ML researchers to date. The "goal" field refers to the presence of heart disease in the patient. It is integer valued with 0 as no presence of heart disease and 1 for presence of heart disease. Experiments with the Cleveland database have concentrated on simply attempting to distinguish presence (values 1) from absence (value 0). The names and social security numbers of the patients were recently removed from the database, replaced with dummy values. One file has been "processed", that one containing the Cleveland database. All four unprocessed files also exist in this directory.</div>', unsafe_allow_html=True)
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
# Missing Values
|
| 13 |
+
st.header("Missing Values")
|
| 14 |
+
st.write("Yes")
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
# Add a footer
|
| 17 |
+
st.markdown("---")
|
| 18 |
+
st.write("Made with ❤️ by Viga, Hanum, & Robit")
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 21 |
+
run()
|
pages/3_Variables_Table.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
import streamlit as st
|
| 2 |
+
import pandas as pd
|
| 3 |
+
|
| 4 |
+
def run():
|
| 5 |
+
st.set_page_config(page_title="Variables Table", layout="wide")
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
st.title("Variables Table")
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
# Define the data for the variables table
|
| 10 |
+
data = {
|
| 11 |
+
"Variable Name": ["age", "sex", "cp", "trestbps", "chol", "fbs", "restecg", "thalach", "exang", "oldpeak", "slope", "ca", "thal", "num"],
|
| 12 |
+
"Role": ["Feature", "Feature", "Feature", "Feature", "Feature", "Feature", "Feature", "Feature", "Feature", "Feature", "Feature", "Feature", "Feature", "Target"],
|
| 13 |
+
"Type": ["Integer", "Categorical", "Categorical", "Integer", "Integer", "Categorical", "Categorical", "Integer", "Categorical", "Integer", "Categorical", "Integer", "Categorical", "Integer"],
|
| 14 |
+
"Demographic": ["Age", "Sex", None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None],
|
| 15 |
+
"Description": [None, None, None, "Resting blood pressure (on admission to the hospital)", "Serum cholestoral", "Fasting blood sugar > 120 mg/dl", None, "Maximum heart rate achieved", "Exercise induced angina", "ST depression induced by exercise relative to rest", None, "Number of major vessels (0-3) colored by flourosopy", None, "Diagnosis of heart disease"],
|
| 16 |
+
"Units": ["years", None, None, "mm Hg", "mg/dl", None, None, "beats per minute", None, None, None, None, None, None],
|
| 17 |
+
"Missing Values": ["no", "no", "no", "no", "no", "no", "no", "no", "no", "no", "no", "yes", "yes", "no"]
|
| 18 |
+
}
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
# Create DataFrame from the data
|
| 21 |
+
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
# Display the DataFrame as a table with larger size
|
| 24 |
+
st.table(df.style.set_table_styles([{'selector': 'tr:hover','props': [('background-color', '#95caff')]}]))
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
# Add a footer
|
| 27 |
+
st.markdown("---")
|
| 28 |
+
st.write("Made with ❤️ by Viga, Hanum, & Robit")
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 31 |
+
run()
|
pages/4_Decision_Tree_Classification.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
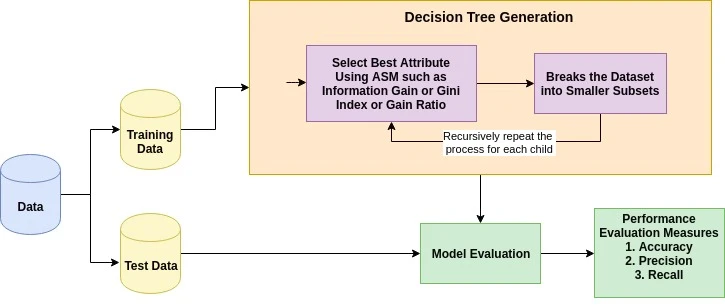
| 1 |
+
import streamlit as st
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
def main():
|
| 4 |
+
st.set_page_config(page_title="Decision Tree Classification", layout="wide")
|
| 5 |
+
|
| 6 |
+
st.title("Decision Tree Classification")
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
# Introduction to Decision Tree
|
| 9 |
+
st.header("The Decision Tree Algorithm")
|
| 10 |
+
st.markdown("""
|
| 11 |
+
A decision tree is a flowchart-like tree structure where an internal node represents a feature (or attribute), the branch represents a decision rule, and each leaf node represents the outcome.
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
The topmost node in a decision tree is known as the root node. It learns to partition on the basis of the attribute value. It partitions the tree in a recursive manner called recursive partitioning. This flowchart-like structure helps you in decision-making. It's visualization like a flowchart diagram which easily mimics the human level thinking. That is why decision trees are easy to understand and interpret.
|
| 14 |
+
""")
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
st.image("The Decision Tree Algorithm.png")
|
| 17 |
+
|
| 18 |
+
st.markdown("""
|
| 19 |
+
A decision tree is a white box type of ML algorithm. It shares internal decision-making logic, which is not available in the black box type of algorithms such as with a neural network. Its training time is faster compared to the neural network algorithm.
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
The time complexity of decision trees is a function of the number of records and attributes in the given data. The decision tree is a distribution-free or non-parametric method which does not depend upon probability distribution assumptions. Decision trees can handle high-dimensional data with good accuracy.
|
| 22 |
+
""")
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
# How Does the Decision Tree Algorithm Work?
|
| 25 |
+
st.header("How Does the Decision Tree Algorithm Work?")
|
| 26 |
+
st.markdown("""
|
| 27 |
+
The basic idea behind any decision tree algorithm is as follows:
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
- Select the best attribute using Attribute Selection Measures (ASM) to split the records.
|
| 30 |
+
- Make that attribute a decision node and breaks the dataset into smaller subsets.
|
| 31 |
+
- Start tree building by repeating this process recursively for each child until one of the conditions will match:
|
| 32 |
+
- All the tuples belong to the same attribute value.
|
| 33 |
+
- There are no more remaining attributes.
|
| 34 |
+
- There are no more instances.
|
| 35 |
+
""")
|
| 36 |
+
|
| 37 |
+
st.image("Decision Tree Algorithm.webp")
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
# Attribute Selection Measures
|
| 40 |
+
st.header("Attribute Selection Measures")
|
| 41 |
+
st.markdown("""
|
| 42 |
+
Attribute selection measure is a heuristic for selecting the splitting criterion that partitions data in the best possible manner. It is also known as splitting rules because it helps us to determine breakpoints for tuples on a given node. ASM provides a rank to each feature (or attribute) by explaining the given dataset. The best score attribute will be selected as a splitting attribute. In the case of a continuous-valued attribute, split points for branches also need to define. The most popular selection measures are Information Gain, Gain Ratio, and Gini Index.
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
**Gini index**
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
Another decision tree algorithm CART (Classification and Regression Tree) uses the Gini method to create split points.
|
| 47 |
+
""")
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
st.image("Gini method.webp")
|
| 50 |
+
|
| 51 |
+
st.markdown("""
|
| 52 |
+
The Gini Index considers a binary split for each attribute. You can compute a weighted sum of the impurity of each partition. If a binary split on attribute A partitions data D into D1 and D2, the Gini index of D is calculated, and the attribute with the minimum Gini index is chosen as the splitting attribute.
|
| 53 |
+
""")
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
st.image("The Gini Index.webp")
|
| 56 |
+
|
| 57 |
+
st.image("smaller gini index.webp")
|
| 58 |
+
|
| 59 |
+
# YouTube Video for additional content
|
| 60 |
+
st.header("Learn More Through This Video")
|
| 61 |
+
st.video("https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_L39rN6gz7Y")
|
| 62 |
+
|
| 63 |
+
# Add a footer
|
| 64 |
+
st.markdown("---")
|
| 65 |
+
st.write("Made with ❤️ by Viga, Hanum, & Robit")
|
| 66 |
+
|
| 67 |
+
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 68 |
+
main()
|
pages/5_Heart_Disease_Prediction.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
import streamlit as st
|
| 2 |
+
import joblib
|
| 3 |
+
|
| 4 |
+
# Set page configuration
|
| 5 |
+
st.set_page_config(page_title="Heart Disease Prediction", layout="wide")
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
# Load the trained model
|
| 8 |
+
model = joblib.load("./model-3.joblib")
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
# Define function to predict heart disease
|
| 11 |
+
def predict_heart_disease(sex, exang, cp_1, cp_2, cp_4, slope_1, slope_2, thal_3, thal_7):
|
| 12 |
+
print([[sex, exang, cp_1, cp_2, cp_4, slope_1, slope_2, thal_3, thal_7]])
|
| 13 |
+
prediction = model.predict([[sex, exang, cp_1, cp_2, cp_4, slope_1, slope_2, thal_3, thal_7]])
|
| 14 |
+
return prediction
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
def run():
|
| 17 |
+
st.title("Heart Disease Prediction")
|
| 18 |
+
st.write("Please provide the following information to predict heart disease:")
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
# Design user interface
|
| 21 |
+
col1, col2 = st.columns([2, 1])
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
with col1:
|
| 24 |
+
sex = st.selectbox("Sex", ["Female", "Male"])
|
| 25 |
+
exang = st.selectbox("Exercise Induced Angina", ["No", "Yes"])
|
| 26 |
+
cp = st.selectbox("Chest Pain Type", ["Typical Angina", "Atypical Angina", "Non-Anginal Pain", "Asymptomatic"])
|
| 27 |
+
slope = st.selectbox("Slope of Peak Exercise ST Segment", ["Upsloping", "Flat", "Downsloping"])
|
| 28 |
+
thal = st.selectbox("Thal", ["Normal", "Fixed Defect", "Reversible Defect"])
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
with col2:
|
| 31 |
+
st.image("https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1618939304347-e91b1f33d2ab?q=80&w=1974&auto=format&fit=crop&ixlib=rb-4.0.3&ixid=M3wxMjA3fDB8MHxwaG90by1wYWdlfHx8fGVufDB8fHx8fA%3D%3D", width=275)
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
# Map selected options to numerical values
|
| 34 |
+
sex_mapping = {"Female": 0, "Male": 1}
|
| 35 |
+
exang_mapping = {"No": 0, "Yes": 1}
|
| 36 |
+
cp_1_mapping = {"Typical Angina": 1, "Atypical Angina": 0, "Non-Anginal Pain": 0, "Asymptomatic": 0}
|
| 37 |
+
cp_2_mapping = {"Typical Angina": 0, "Atypical Angina": 1, "Non-Anginal Pain": 0, "Asymptomatic": 0}
|
| 38 |
+
cp_4_mapping = {"Typical Angina": 0, "Atypical Angina": 0, "Non-Anginal Pain": 0, "Asymptomatic": 1}
|
| 39 |
+
slope_1_mapping = {"Upsloping": 1, "Flat": 0, "Downsloping": 0}
|
| 40 |
+
slope_2_mapping = {"Upsloping": 0, "Flat": 1, "Downsloping": 0}
|
| 41 |
+
thal_3_mapping = {"Normal": 1, "Fixed Defect": 0, "Reversible Defect": 0}
|
| 42 |
+
thal_7_mapping = {"Normal": 0, "Fixed Defect": 0, "Reversible Defect": 1}
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
# Predict button
|
| 45 |
+
if st.button("Predict", key="predict_button"):
|
| 46 |
+
result = predict_heart_disease(sex_mapping[sex], exang_mapping[exang], cp_1_mapping[cp], cp_2_mapping[cp], cp_4_mapping[cp], slope_1_mapping[slope], slope_2_mapping[slope], thal_3_mapping[thal], thal_7_mapping[thal])
|
| 47 |
+
if result == 1:
|
| 48 |
+
st.error("The model predicts that the patient has heart disease.")
|
| 49 |
+
else:
|
| 50 |
+
st.success("The model predicts that the patient does not have heart disease.")
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
# Add a footer
|
| 53 |
+
st.markdown("---")
|
| 54 |
+
st.write("Made with ❤️ by Viga, Hanum, & Robit")
|
| 55 |
+
|
| 56 |
+
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 57 |
+
run()
|
pages/__pycache__/about.cpython-311.pyc
ADDED
|
Binary file (677 Bytes). View file
|
|
|
pages/__pycache__/genetic_algorithm.cpython-311.pyc
ADDED
|
Binary file (2.84 kB). View file
|
|
|
smaller gini index.webp
ADDED
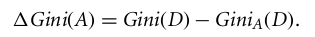
|