metadata
license: other
license_name: glm-4
license_link: >-
https://modelscope.cn/models/ZhipuAI/glm-4-9b-chat/file/view/master?fileName=LICENSE&status=0
language:
- zh
- en
tags:
- glm
- chatglm
- thudm
inference: false
GLM-4-9B-Chat
Read this in English.
GLM-4-9B 是智谱 AI 推出的最新一代预训练模型 GLM-4 系列中的开源版本。 在语义、数学、推理、代码和知识等多方面的数据集测评中,GLM-4-9B 及其人类偏好对齐的版本 GLM-4-9B-Chat 均表现出较高的性能。 除了能进行多轮对话,GLM-4-9B-Chat 还具备网页浏览、代码执行、自定义工具调用(Function Call)和长文本推理(支持最大 128K 上下文)等高级功能。 本代模型增加了多语言支持,支持包括日语,韩语,德语在内的 26 种语言。我们还推出了支持 1M 上下文长度(约 200 万中文字符)的模型。
评测结果
我们在一些经典任务上对 GLM-4-9B-Chat 模型进行了评测,并得到了如下的结果:
| Model | AlignBench-v2 | MT-Bench | IFEval | MMLU | C-Eval | GSM8K | MATH | HumanEval | NCB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 5.12 | 8.00 | 68.58 | 68.4 | 51.3 | 79.6 | 30.0 | 62.2 | 24.7 |
| ChatGLM3-6B | 3.97 | 5.50 | 28.1 | 66.4 | 69.0 | 72.3 | 25.7 | 58.5 | 11.3 |
| GLM-4-9B-Chat | 6.61 | 8.35 | 69.0 | 72.4 | 75.6 | 79.6 | 50.6 | 71.8 | 32.2 |
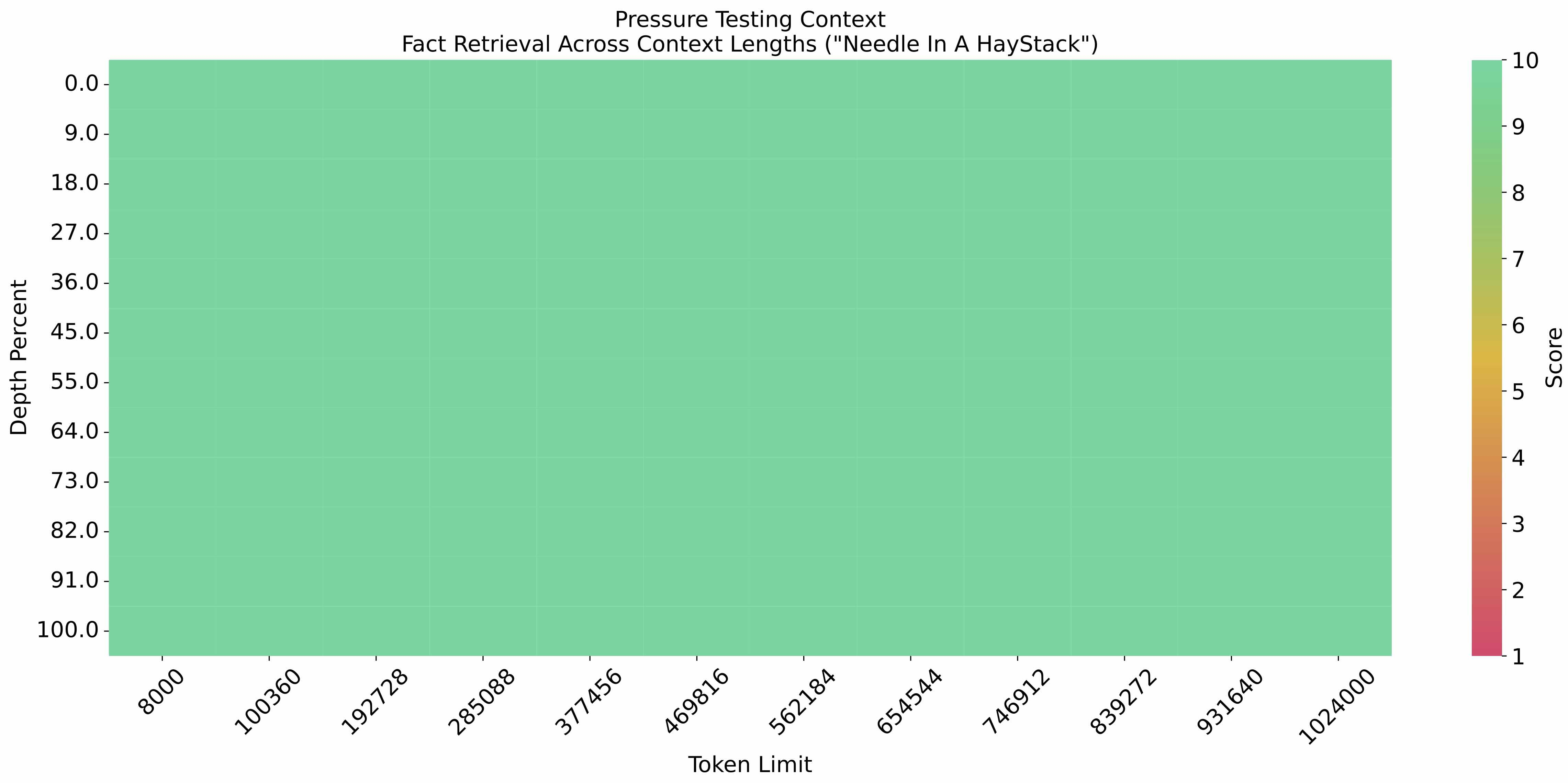
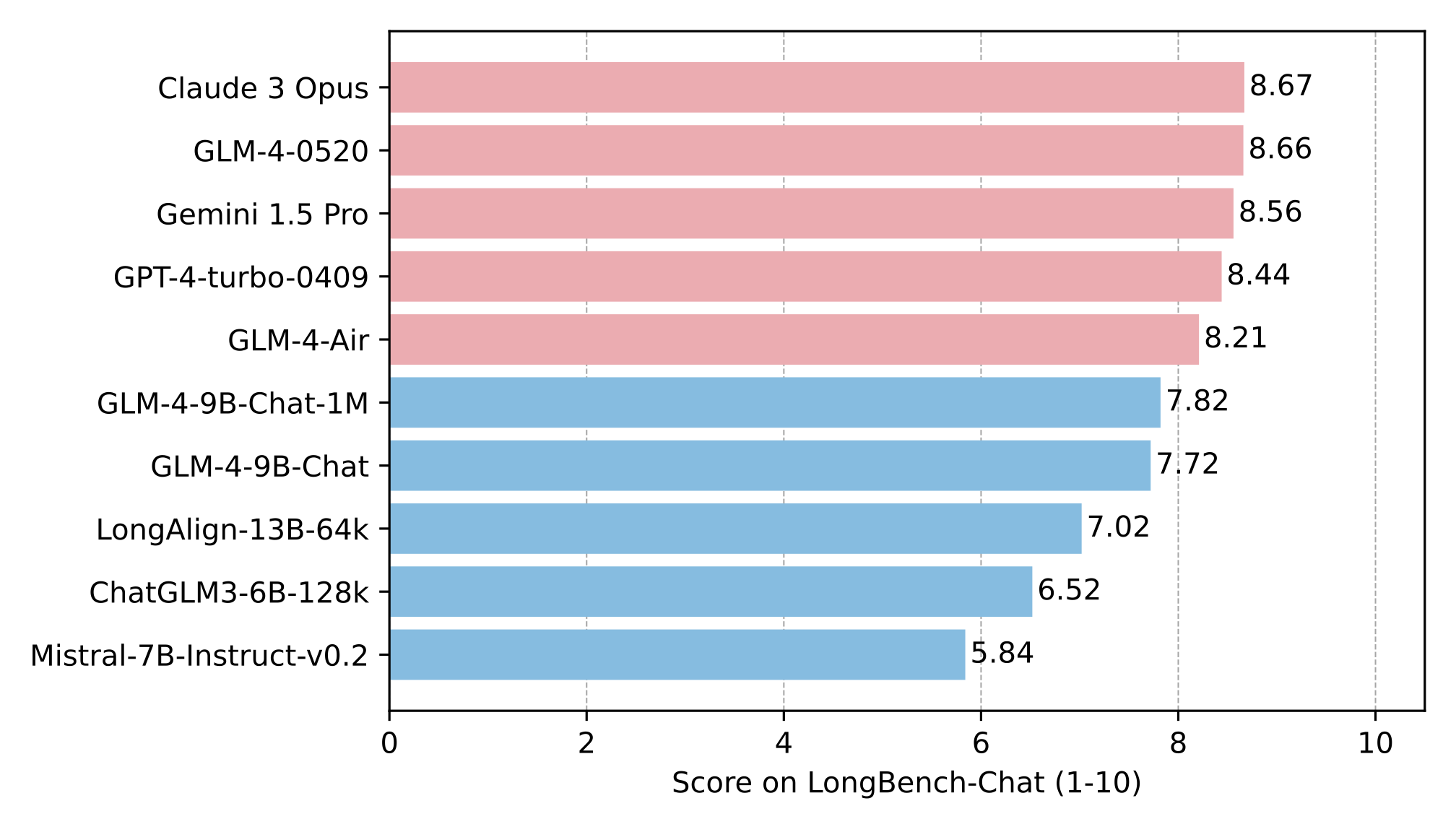
长文本
在 1M 的上下文长度下进行大海捞针实验,结果如下:
在 LongBench-Chat 上对长文本能力进行了进一步评测,结果如下:
多语言能力
在六个多语言数据集上对 GLM-4-9B-Chat 和 Llama-3-8B-Instruct 进行了测试,测试结果及数据集对应选取语言如下表
| Dataset | Llama-3-8B-Instruct | GLM-4-9B-Chat | Languages |
|---|---|---|---|
| M-MMLU | 49.6 | 56.6 | all |
| FLORES | 25.0 | 28.8 | ru, es, de, fr, it, pt, pl, ja, nl, ar, tr, cs, vi, fa, hu, el, ro, sv, uk, fi, ko, da, bg, no |
| MGSM | 54.0 | 65.3 | zh, en, bn, de, es, fr, ja, ru, sw, te, th |
| XWinograd | 61.7 | 73.1 | zh, en, fr, jp, ru, pt |
| XStoryCloze | 84.7 | 90.7 | zh, en, ar, es, eu, hi, id, my, ru, sw, te |
| XCOPA | 73.3 | 80.1 | zh, et, ht, id, it, qu, sw, ta, th, tr, vi |
工具调用能力
我们在 Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard上进行了测试并得到了以下结果:
| Model | Overall Acc. | AST Summary | Exec Summary | Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 58.88 | 59.25 | 70.01 | 45.83 |
| gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09 | 81.24 | 82.14 | 78.61 | 88.75 |
| ChatGLM3-6B | 57.88 | 62.18 | 69.78 | 5.42 |
| GLM-4-9B-Chat | 81.00 | 80.26 | 84.40 | 87.92 |
本仓库是 GLM-4-9B-Chat 的模型仓库,支持128K上下文长度。
运行模型
更多推理代码和依赖信息,请访问我们的 github 。
使用 transformers 后端进行推理:
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
device = "cuda"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat",trust_remote_code=True)
query = "你好"
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template([{"role": "user", "content": query}],
add_generation_prompt=True,
tokenize=True,
return_tensors="pt",
return_dict=True
)
inputs = inputs.to(device)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
trust_remote_code=True
).to(device).eval()
gen_kwargs = {"max_length": 2500, "do_sample": True, "top_k": 1}
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, **gen_kwargs)
outputs = outputs[:, inputs['input_ids'].shape[1]:]
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
使用 vLLM后端进行推理:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
# GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M
# max_model_len, tp_size = 1048576, 4
# GLM-4-9B-Chat
# 如果遇见 OOM 现象,建议减少max_model_len,或者增加tp_size
max_model_len, tp_size = 131072, 1
model_name = "THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat"
prompt = [{"role": "user", "content": "你好"}]
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True)
llm = LLM(
model=model_name,
tensor_parallel_size=tp_size,
max_model_len=max_model_len,
trust_remote_code=True,
enforce_eager=True,
# GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M 如果遇见 OOM 现象,建议开启下述参数
# enable_chunked_prefill=True,
# max_num_batched_tokens=8192
)
stop_token_ids = [151329, 151336, 151338]
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.95, max_tokens=1024, stop_token_ids=stop_token_ids)
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(prompt, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
outputs = llm.generate(prompts=inputs, sampling_params=sampling_params)
print(outputs[0].outputs[0].text)
协议
GLM-4 模型的权重的使用则需要遵循 LICENSE。
引用
如果你觉得我们的工作有帮助的话,请考虑引用下列论文。
@misc{glm2024chatglm,
title={ChatGLM: A Family of Large Language Models from GLM-130B to GLM-4 All Tools},
author={Team GLM and Aohan Zeng and Bin Xu and Bowen Wang and Chenhui Zhang and Da Yin and Diego Rojas and Guanyu Feng and Hanlin Zhao and Hanyu Lai and Hao Yu and Hongning Wang and Jiadai Sun and Jiajie Zhang and Jiale Cheng and Jiayi Gui and Jie Tang and Jing Zhang and Juanzi Li and Lei Zhao and Lindong Wu and Lucen Zhong and Mingdao Liu and Minlie Huang and Peng Zhang and Qinkai Zheng and Rui Lu and Shuaiqi Duan and Shudan Zhang and Shulin Cao and Shuxun Yang and Weng Lam Tam and Wenyi Zhao and Xiao Liu and Xiao Xia and Xiaohan Zhang and Xiaotao Gu and Xin Lv and Xinghan Liu and Xinyi Liu and Xinyue Yang and Xixuan Song and Xunkai Zhang and Yifan An and Yifan Xu and Yilin Niu and Yuantao Yang and Yueyan Li and Yushi Bai and Yuxiao Dong and Zehan Qi and Zhaoyu Wang and Zhen Yang and Zhengxiao Du and Zhenyu Hou and Zihan Wang},
year={2024},
eprint={2406.12793},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={id='cs.CL' full_name='Computation and Language' is_active=True alt_name='cmp-lg' in_archive='cs' is_general=False description='Covers natural language processing. Roughly includes material in ACM Subject Class I.2.7. Note that work on artificial languages (programming languages, logics, formal systems) that does not explicitly address natural-language issues broadly construed (natural-language processing, computational linguistics, speech, text retrieval, etc.) is not appropriate for this area.'}
}