Enbeddrus v0.1 D+PC - English and Russian embedder
This is the model trained on Domain then on Parallel Corpora, other model is here.
This is a BERT (uncased) sentence-transformers model: It maps sentences & paragraphs to a 768 dimensional dense vector space and can be used for tasks like clustering or semantic search.
- Parameters: 168 million
- Layers: 12
- Hidden Size: 768
- Attention Heads: 12
- Vocabulary Size: 119,547
- Maximum Sequence Length: 512 tokens
The Enbeddrus model is designed to extract similar embeddings for comparable English and Russian phrases. It is based on the bert-base-multilingual-uncased model and was trained over 20 epochs on the following datasets:
- evilfreelancer/opus-php-en-ru-cleaned ( train): 1.6k lines
- Helsinki-NLP/opus_books (en-ru, train): 17.5k lines
The goal of this model is to generate identical or very similar embeddings regardless of whether the text is written in English or Russian.
Enbeddrus GGUF version available via Ollama.
Usage (Sentence-Transformers)
Using this model becomes easy when you have sentence-transformers installed:
pip install -U sentence-transformers
Then you can use the model like this:
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
sentences = [
"PHP является скриптовым языком программирования, широко используемым для веб-разработки.",
"PHP is a scripting language widely used for web development.",
"PHP поддерживает множество баз данных, таких как MySQL, PostgreSQL и SQLite.",
"PHP supports many databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite.",
"Функция echo в PHP используется для вывода текста на экран.",
"The echo function in PHP is used to output text to the screen.",
"Машинное обучение помогает создавать интеллектуальные системы.",
"Machine learning helps to create intelligent systems.",
]
model = SentenceTransformer('evilfreelancer/enbeddrus-v0.1-domain')
embeddings = model.encode(sentences)
print(embeddings)
Usage (HuggingFace Transformers)
Without sentence-transformers, you can use the model like this: First, you pass your input through the transformer model, then you have to apply the right pooling-operation on-top of the contextualized word embeddings.
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
import torch
# Mean Pooling - Take attention mask into account for correct averaging
def mean_pooling(model_output, attention_mask):
token_embeddings = model_output[0] # First element of model_output contains all token embeddings
input_mask_expanded = attention_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand(token_embeddings.size()).float()
return torch.sum(token_embeddings * input_mask_expanded, 1) / torch.clamp(input_mask_expanded.sum(1), min=1e-9)
# Sentences we want sentence embeddings for
sentences = [
"PHP является скриптовым языком программирования, широко используемым для веб-разработки.",
"PHP is a scripting language widely used for web development.",
"PHP поддерживает множество баз данных, таких как MySQL, PostgreSQL и SQLite.",
"PHP supports many databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite.",
"Функция echo в PHP используется для вывода текста на экран.",
"The echo function in PHP is used to output text to the screen.",
"Машинное обучение помогает создавать интеллектуальные системы.",
"Machine learning helps to create intelligent systems.",
]
# Load model from HuggingFace Hub
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('evilfreelancer/enbeddrus-v0.1-domain')
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained('evilfreelancer/enbeddrus-v0.1-domain')
# Tokenize sentences
encoded_input = tokenizer(sentences, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors='pt')
# Compute token embeddings
with torch.no_grad():
model_output = model(**encoded_input)
# Perform pooling. In this case, mean pooling.
sentence_embeddings = mean_pooling(model_output, encoded_input['attention_mask'])
print("Sentence embeddings:")
print(sentence_embeddings)
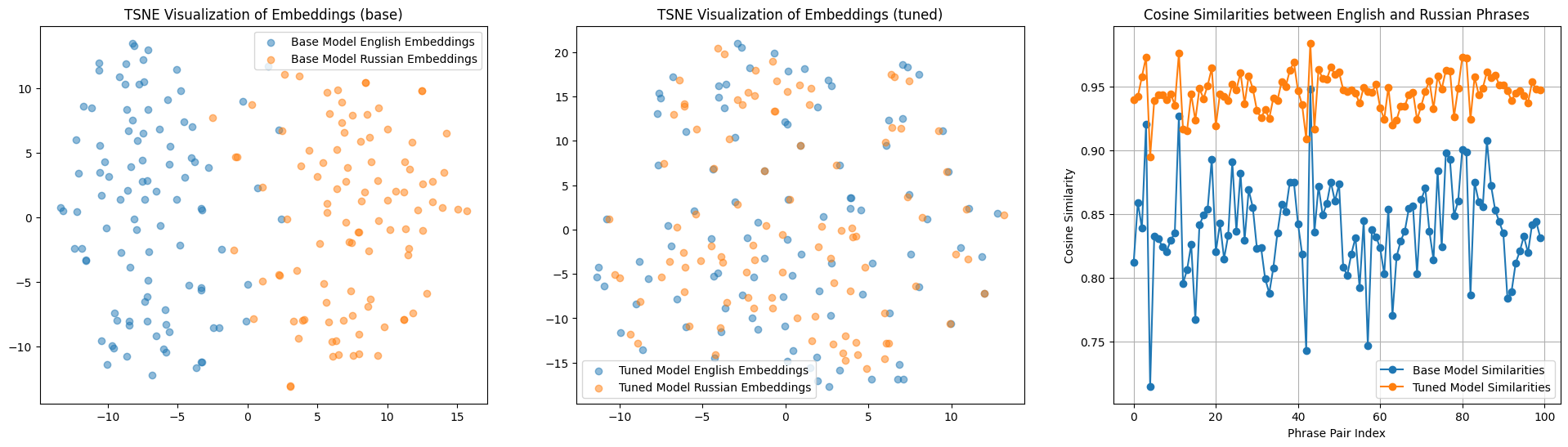
Evaluation Results
The model was tested on the eval split of the
dataset evilfreelancer/opus-php-en-ru-cleaned,
which contains 100 pairs of sentences in Russian and English on the topic of PHP. The results of the testing are
presented in the image below.
- Left: Embedding similarity in Russian and English before training (the points are spread out into two distinct clusters).
- Center: Embedding similarity after training (the points representing similar phrases are very close to each other).
- Right: Cosine distance before and after training.
Training
The model was trained with the parameters:
DataLoader:
torch.utils.data.dataloader.DataLoader of length 556 with parameters:
{
'batch_size': 64,
'sampler': 'torch.utils.data.sampler.RandomSampler',
'batch_sampler': 'torch.utils.data.sampler.BatchSampler'
}
Loss:
sentence_transformers.losses.MSELoss.MSELoss
Parameters of the fit()-Method:
{
"epochs": 20,
"evaluation_steps": 100,
"evaluator": "sentence_transformers.evaluation.SequentialEvaluator.SequentialEvaluator",
"max_grad_norm": 1,
"optimizer_class": "<class 'torch.optim.adamw.AdamW'>",
"optimizer_params": {
"eps": 1e-06,
"lr": 2e-05
},
"scheduler": "WarmupLinear",
"steps_per_epoch": null,
"warmup_steps": 10000,
"weight_decay": 0.01
}
Full Model Architecture
SentenceTransformer(
(0): Transformer({'max_seq_length': 512, 'do_lower_case': False}) with Transformer model: BertModel
(1): Pooling({'word_embedding_dimension': 768, 'pooling_mode_cls_token': False, 'pooling_mode_mean_tokens': True, 'pooling_mode_max_tokens': False, 'pooling_mode_mean_sqrt_len_tokens': False, 'pooling_mode_weightedmean_tokens': False, 'pooling_mode_lasttoken': False, 'include_prompt': True})
)
Citing & Authors
- Downloads last month
- 44