language:
- en
datasets:
- c4
license: apache-2.0
Introduction
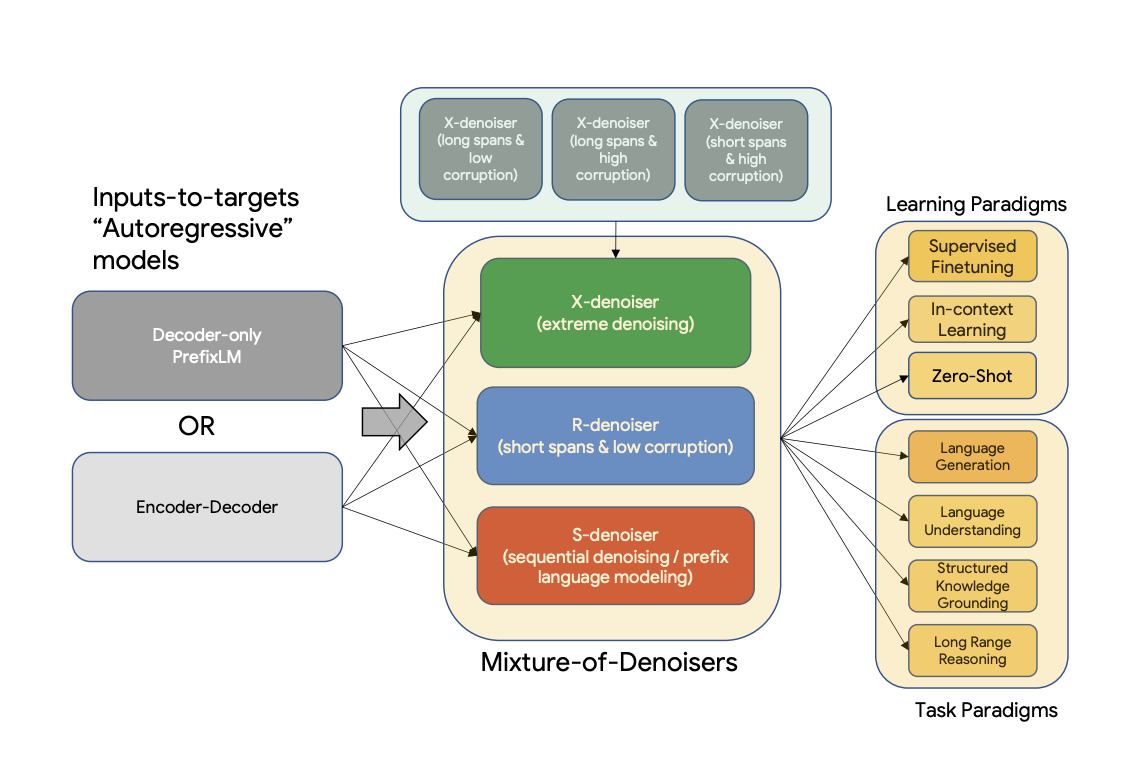
UL2 is a unified framework for pretraining models that are universally effective across datasets and setups. UL2 uses Mixture-of-Denoisers (MoD), apre-training objective that combines diverse pre-training paradigms together. UL2 introduces a notion of mode switching, wherein downstream fine-tuning is associated with specific pre-training schemes.
Abstract
Existing pre-trained models are generally geared towards a particular class of problems. To date, there seems to be still no consensus on what the right architecture and pre-training setup should be. This paper presents a unified framework for pre-training models that are universally effective across datasets and setups. We begin by disentangling architectural archetypes with pre-training objectives -- two concepts that are commonly conflated. Next, we present a generalized and unified perspective for self-supervision in NLP and show how different pre-training objectives can be cast as one another and how interpolating between different objectives can be effective. We then propose Mixture-of-Denoisers (MoD), a pre-training objective that combines diverse pre-training paradigms together. We furthermore introduce a notion of mode switching, wherein downstream fine-tuning is associated with specific pre-training schemes. We conduct extensive ablative experiments to compare multiple pre-training objectives and find that our method pushes the Pareto-frontier by outperforming T5 and/or GPT-like models across multiple diverse setups. Finally, by scaling our model up to 20B parameters, we achieve SOTA performance on 50 well-established supervised NLP tasks ranging from language generation (with automated and human evaluation), language understanding, text classification, question answering, commonsense reasoning, long text reasoning, structured knowledge grounding and information retrieval. Our model also achieve strong results at in-context learning, outperforming 175B GPT-3 on zero-shot SuperGLUE and tripling the performance of T5-XXL on one-shot summarization.
For more information, please take a look at the original paper.
Paper: Unifying Language Learning Paradigms
Authors: Yi Tay, Mostafa Dehghani, Vinh Q. Tran, Xavier Garcia, Dara Bahri, Tal Schuster, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Neil Houlsby, Donald Metzler
Training
The checkpoint was iteratively pre-trained on C4 and fine-tuned on a variety of datasets
PreTraining
The model is pretrained on the C4 corpus. For pretraining, the model is trained on a total of 1 trillion tokens on C4 (2 million steps)
with a batch size of 1024. The sequence length is set to 512/512 for inputs and targets.
Dropout is set to 0 during pretraining. Pre-training took slightly more than one month for about 1 trillion
tokens. The model has 32 encoder layers and 32 decoder layers, dmodel of 4096 and df of 16384.
The dimension of each head is 256 for a total of 16 heads. Our model uses a model parallelism of 8.
The same same sentencepiece tokenizer as T5 of vocab size 32000 is used (click here for more information about the T5 tokenizer).
UL-20B can be interpreted as a model that is quite similar to T5 but trained with a different objective and slightly different scaling knobs. UL-20B was trained using the Jax and T5X infrastructure.
The training objective during pretraining is a mixture of different denoising strategies that are explained in the following:
Mixture of Denoisers
To quote the paper:
We conjecture that a strong universal model has to be exposed to solving diverse set of problems during pre-training. Given that pre-training is done using self-supervision, we argue that such diversity should be injected to the objective of the model, otherwise the model might suffer from lack a certain ability, like long-coherent text generation. Motivated by this, as well as current class of objective functions, we define three main paradigms that are used during pre-training:
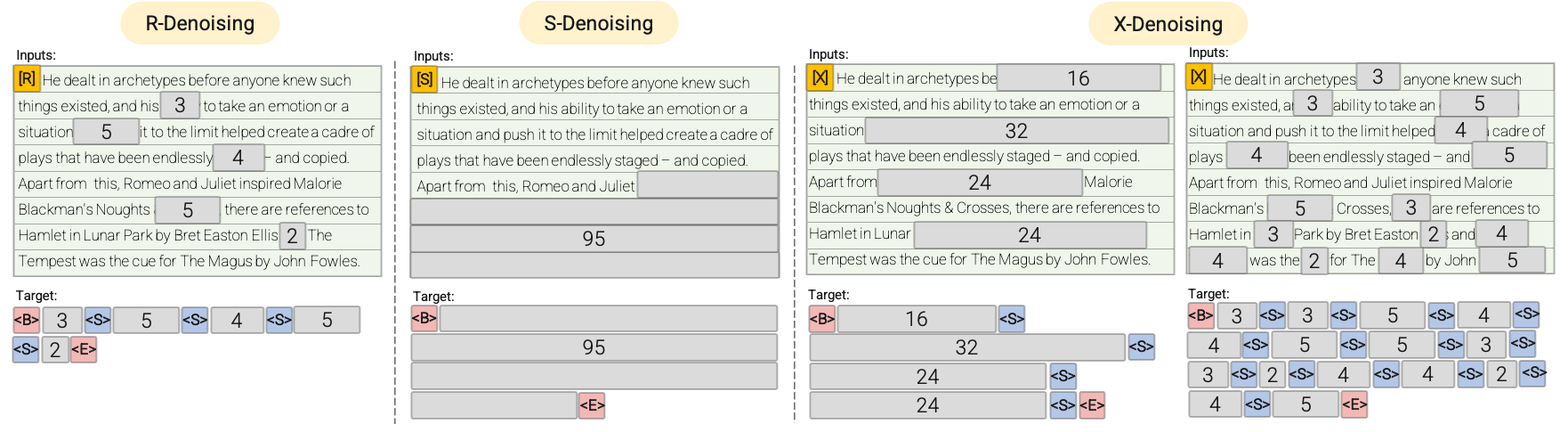
R-Denoiser: The regular denoising is the standard span corruption introduced in T5 that uses a range of 2 to 5 tokens as the span length, which masks about 15% of input tokens. These spans are short and potentially useful to acquire knowledge instead of learning to generate fluent text.
S-Denoiser: A specific case of denoising where we observe a strict sequential order when framing the inputs-to-targets task, i.e., prefix language modeling. To do so, we simply partition the input sequence into two sub-sequences of tokens as context and target such that the targets do not rely on future information. This is unlike standard span corruption where there could be a target token with earlier position than a context token. Note that similar to the Prefix-LM setup, the context (prefix) retains a bidirectional receptive field. We note that S-Denoising with very short memory or no memory is in similar spirit to standard causal language modeling.
X-Denoiser: An extreme version of denoising where the model must recover a large part of the input, given a small to moderate part of it. This simulates a situation where a model needs to generate long target from a memory with relatively limited information. To do so, we opt to include examples with aggressive denoising where approximately 50% of the input sequence is masked. This is by increasing the span length and/or corruption rate. We consider a pre-training task to be extreme if it has a long span (e.g., ≥ 12 tokens) or have a large corruption rate (e.g., ≥ 30%). X-denoising is motivated by being an interpolation between regular span corruption and language model like objectives.
See the following diagram for a more visual explanation:
Important: For more details, please see sections 3.1.2 of the paper.
Fine-tuning
The model was continously fine-tuned after N pretraining steps where N is typically from 50k to 100k. In other words, after each Nk steps of pretraining, the model is finetuned on each downstream task. See section 5.2.2 of paper to get an overview of all datasets that were used for fine-tuning).
As the model is continuously finetuned, finetuning is stopped on a task once it has reached state-of-the-art to save compute. In total, the model was trained for 2.65 million steps.
Important: For more details, please see sections 5.2.1 and 5.2.2 of the paper.
Contribution
This model was contributed by Daniel Hesslow.
Examples
The following shows how one can predict masked passages using the different denoising strategies.
from transformers import T5ForConditionalGeneration, AutoTokenizer
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Seledorn/ul2", low_cpu_mem_usage=True, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Seledorn/ul2")
Example usage
inps = ["""
Mr. and Mrs. Dursley, of number four, Privet Drive, <extra_id_0> the last people you'd expect to be involved in anything strange or mysterious, because they just didn't hold with such nonsense.
Mr. Dursley was the director of a firm called Grunnings, which made drills. He was a big, <extra_id_1>. Mrs. Dursley was thin and blonde and had nearly twice the usual amount of neck, which came in very useful as she spent so much of her time craning over garden fences, spying on the neighbours. The Dursleys had a small son called Dudley and in their opinion there was no finer boy anywhere.
The Dursleys had everything they wanted, but they also had a secret, and their greatest fear was that somebody would discover it. They didn't think they could bear it if anyone found out about the Potters. Mrs. Potter was Mrs. Dursley's sister, but they hadn't met for several years; in fact, Mrs. Dursley pretended she didn't have a sister, because her sister and her good-for-nothing husband were as unDursleyish as it was possible to be. The Dursleys shuddered to think what the neighbours would say if the Potters arrived in the street. The Dursleys knew that the Potters had a small son, too, but they had never even seen him. This boy was another good reason for keeping the Potters away; they didn't want Dudley mixing with a child like that."""
]
Note use `[NLG]` for X-denoisers, `[NLU]` for R-denoisers and `[S2S]` for S-Denoisers.
model.cuda()
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for inp in inps:
inputs = tokenizer(inp, return_tensors="pt").input_ids
inputs_ = inputs.cuda()
outputs = model.generate(inputs_, max_length = 200, do_sample=True, temperature = 0.9, num_return_sequences=4)
for output in outputs:
out = tokenizer.decode(output)
inps = re.split(pattern, inp)
outs = re.split(pattern, out)
l = [z for (x,y) in zip(inps, outs[1:len(inps)]+ [""]) for z in (x,"*"+y+"*" if y != "" else "")]
print("".join(l))
print("-------------------------------")
Example output
Mr. and Mrs. Dursley, of number four, Privet Drive, were the last people you'd expect to be involved in anything strange or mysterious, because they just didn't hold with such nonsense.
Mr. Dursley was the director of a firm called Grunnings, which made drills. He was a big, solid man with a short, brown beard, an enormous head full of brains and a round, fat face. He had a voice, too, that was so deep that it was nearly always accompanied by a slight tremor... Mrs. Dursley was thin and blonde and had nearly twice the usual amount of neck, which came in very useful as she spent so much of her time craning over garden fences, spying on the neighbours. The Dursleys had a small son called Dudley and in their opinion there was no finer boy anywhere.
The Dursleys had everything they wanted, but they also had a secret, and their greatest fear was that somebody would discover it. They didn't think they could bear it if anyone found out about the Potters. Mrs. Potter was Mrs. Dursley's sister, but they hadn't met for several years; in fact, Mrs. Dursley pretended she didn't have a sister, because her sister and her good-for-nothing husband were as unDursleyish as it was possible to be. The Dursleys shuddered to think what the neighbours would say if the Potters arrived in the street. The Dursleys knew that the Potters had a small son, too, but they had never even seen him. This boy was another good reason for keeping the Potters away; they didn't want Dudley mixing with a child like that.
Where bold is the completion of the model.