Kandinsky 2.1
Kandinsky 2.1 inherits best practices from Dall-E 2 and Latent diffusion while introducing some new ideas.
It uses the CLIP model as a text and image encoder, and diffusion image prior (mapping) between latent spaces of CLIP modalities. This approach increases the visual performance of the model and unveils new horizons in blending images and text-guided image manipulation.
The Kandinsky model is created by Arseniy Shakhmatov, Anton Razzhigaev, Aleksandr Nikolich, Igor Pavlov, Andrey Kuznetsov and Denis Dimitrov
Usage
Kandinsky 2.1 is available in diffusers!
pip install diffusers transformers
Text to image
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
import torch
pipe = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
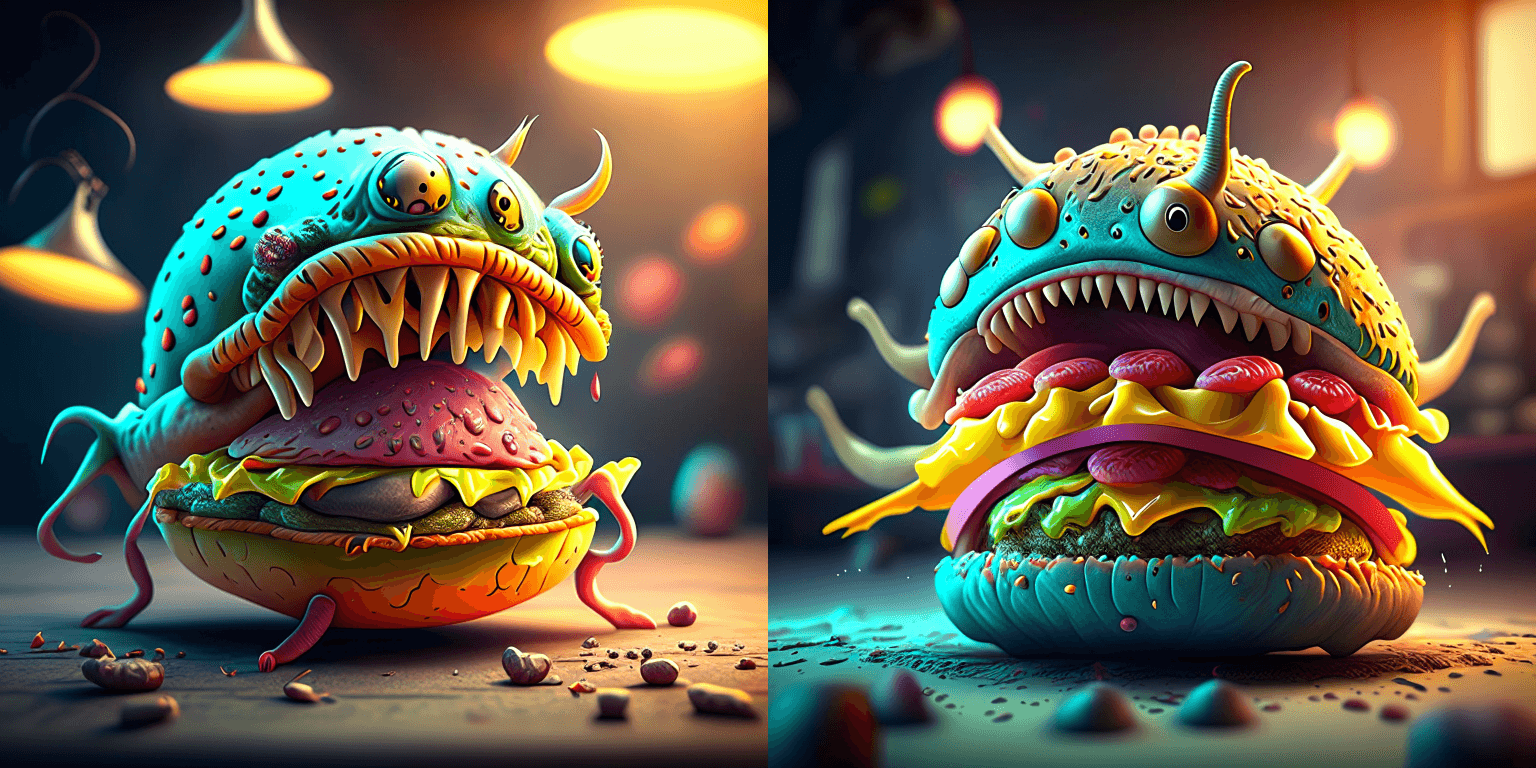
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, prior_guidance_scale =1.0, height=768, width=768).images[0]
image.save("cheeseburger_monster.png")
Text Guided Image-to-Image Generation
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForImage2Image
import torch
import requests
from io import BytesIO
from PIL import Image
import os
pipe = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, Cinematic lighting"
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
response = requests.get(url)
original_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
original_image.thumbnail((768, 768))
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=original_image, strength=0.3).images[0]
out.images[0].save("fantasy_land.png")
Text Guided Inpainting Generation
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForInpainting
from diffusers.utils import load_image
import torch
import numpy as np
pipe = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-inpaint", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
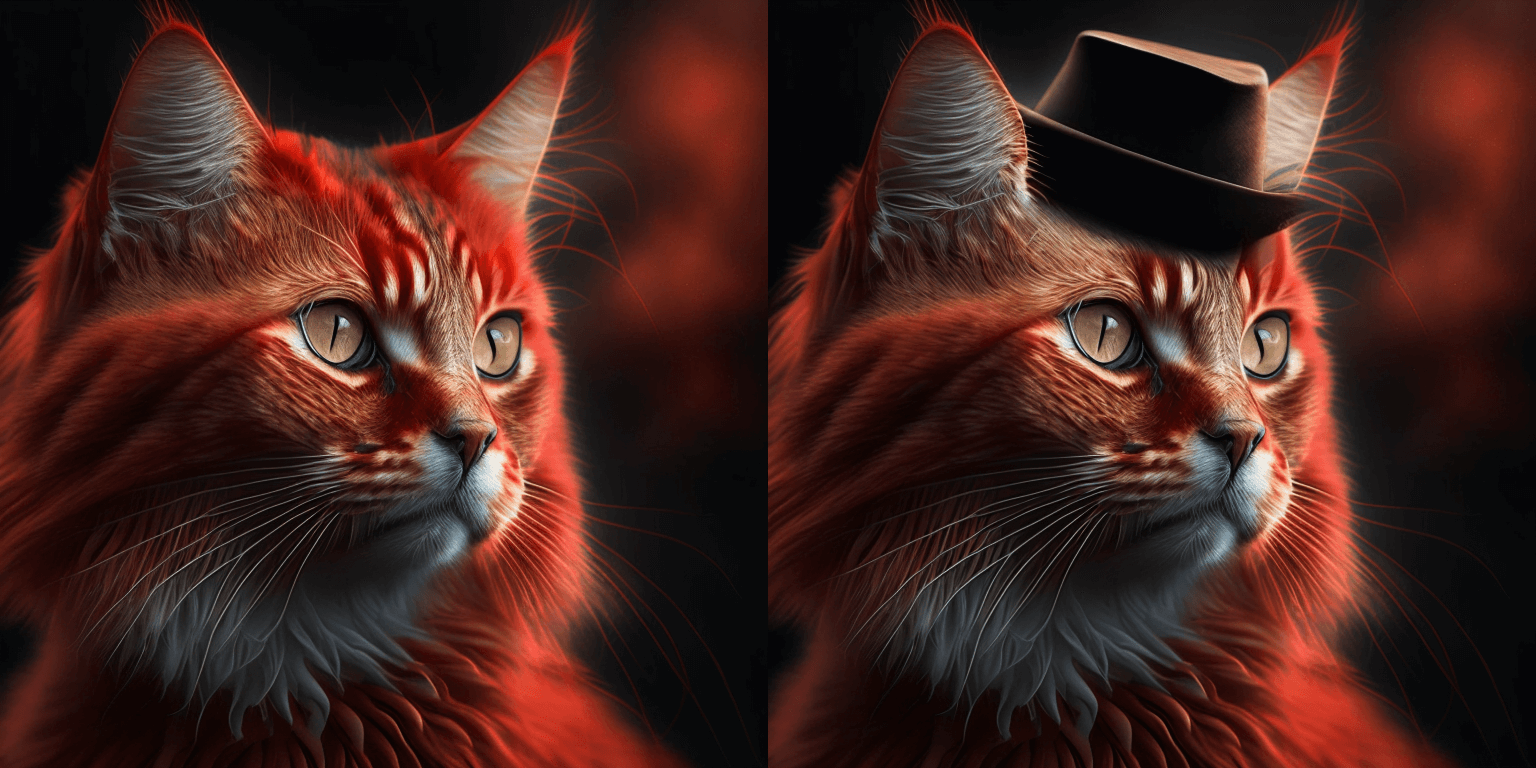
prompt = "a hat"
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
original_image = load_image(
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main" "/kandinsky/cat.png"
)
mask = np.zeros((768, 768), dtype=np.float32)
# Let's mask out an area above the cat's head
mask[:250, 250:-250] = 1
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=original_image, mask_image=mask).images[0]
image.save("cat_with_hat.png")
🚨🚨🚨 Breaking change for Kandinsky Mask Inpainting 🚨🚨🚨
We introduced a breaking change for Kandinsky inpainting pipeline in the following pull request: https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/4207. Previously we accepted a mask format where black pixels represent the masked-out area. This is inconsistent with all other pipelines in diffusers. We have changed the mask format in Knaindsky and now using white pixels instead. Please upgrade your inpainting code to follow the above. If you are using Kandinsky Inpaint in production. You now need to change the mask to:
# For PIL input
import PIL.ImageOps
mask = PIL.ImageOps.invert(mask)
# For PyTorch and Numpy input
mask = 1 - mask
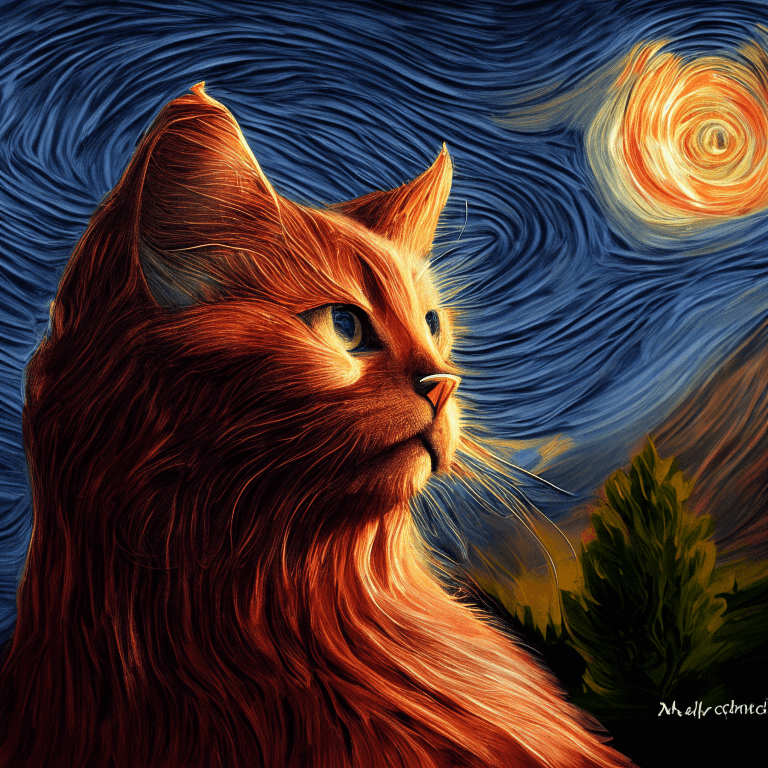
Interpolate
from diffusers import KandinskyPriorPipeline, KandinskyPipeline
from diffusers.utils import load_image
import PIL
import torch
pipe_prior = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
)
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
img1 = load_image(
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main" "/kandinsky/cat.png"
)
img2 = load_image(
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main" "/kandinsky/starry_night.jpeg"
)
# add all the conditions we want to interpolate, can be either text or image
images_texts = ["a cat", img1, img2]
# specify the weights for each condition in images_texts
weights = [0.3, 0.3, 0.4]
# We can leave the prompt empty
prompt = ""
prior_out = pipe_prior.interpolate(images_texts, weights)
pipe = KandinskyPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe.to("cuda")
image = pipe(prompt, **prior_out, height=768, width=768).images[0]
image.save("starry_cat.png")
Model Architecture
Overview
Kandinsky 2.1 is a text-conditional diffusion model based on unCLIP and latent diffusion, composed of a transformer-based image prior model, a unet diffusion model, and a decoder.
The model architectures are illustrated in the figure below - the chart on the left describes the process to train the image prior model, the figure in the center is the text-to-image generation process, and the figure on the right is image interpolation.
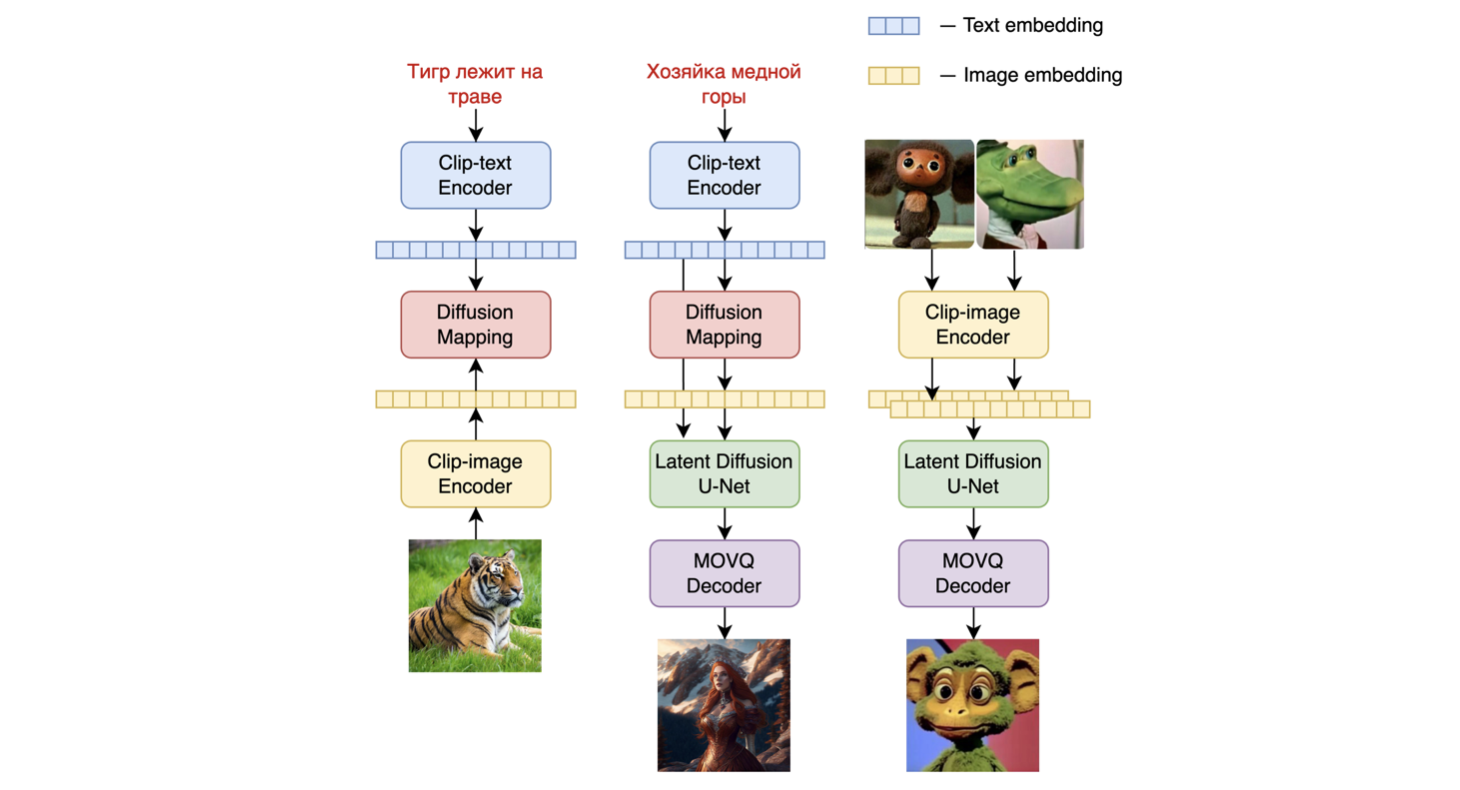
Specifically, the image prior model was trained on CLIP text and image embeddings generated with a pre-trained mCLIP model. The trained image prior model is then used to generate mCLIP image embeddings for input text prompts. Both the input text prompts and its mCLIP image embeddings are used in the diffusion process. A MoVQGAN model acts as the final block of the model, which decodes the latent representation into an actual image.
Details
The image prior training of the model was performed on the LAION Improved Aesthetics dataset, and then fine-tuning was performed on the LAION HighRes data.
The main Text2Image diffusion model was trained on the basis of 170M text-image pairs from the LAION HighRes dataset (an important condition was the presence of images with a resolution of at least 768x768). The use of 170M pairs is due to the fact that we kept the UNet diffusion block from Kandinsky 2.0, which allowed us not to train it from scratch. Further, at the stage of fine-tuning, a dataset of 2M very high-quality high-resolution images with descriptions (COYO, anime, landmarks_russia, and a number of others) was used separately collected from open sources.
Evaluation
We quantitatively measure the performance of Kandinsky 2.1 on the COCO_30k dataset, in zero-shot mode. The table below presents FID.
FID metric values for generative models on COCO_30k
| FID (30k) | |
|---|---|
| eDiff-I (2022) | 6.95 |
| Image (2022) | 7.27 |
| Kandinsky 2.1 (2023) | 8.21 |
| Stable Diffusion 2.1 (2022) | 8.59 |
| GigaGAN, 512x512 (2023) | 9.09 |
| DALL-E 2 (2022) | 10.39 |
| GLIDE (2022) | 12.24 |
| Kandinsky 1.0 (2022) | 15.40 |
| DALL-E (2021) | 17.89 |
| Kandinsky 2.0 (2022) | 20.00 |
| GLIGEN (2022) | 21.04 |
For more information, please refer to the upcoming technical report.
BibTex
If you find this repository useful in your research, please cite:
@misc{kandinsky 2.1,
title = {kandinsky 2.1},
author = {Arseniy Shakhmatov, Anton Razzhigaev, Aleksandr Nikolich, Vladimir Arkhipkin, Igor Pavlov, Andrey Kuznetsov, Denis Dimitrov},
year = {2023},
howpublished = {},
}
- Downloads last month
- 44,420