Spaces:
Sleeping
title: Portiloop Demo
emoji:
'[object Object]': null
colorFrom:
'[object Object]': null
colorTo:
'[object Object]': null
sdk:
'[object Object]': null
sdk_version:
'[object Object]': null
app_file: portiloop/src/demo/demo.py
pinned: false
Portiloop software
This software works with the Coral implementation of the Portiloop EEG closed-loop stimulation device.
It enables controlling the Portiloop from a simple Graphical User Interface (GUI).
Quick links
Usage:
The Portiloop GUI is a web-based interface running as a jupyter server.
- Connect to the
PortiloopWiFi network. - Open your favorite web browser
- Enter the following address:
192.168.0.1:9000
You should now be connected to the jupyter server.
If the jupyter notebook is not yet created:
- Hit
Newand selectPython 3.
This creates a jupyter notebook, in which you can simply paste and execute te following:
from portiloop.capture import Capture
cap = Capture()
When the jupyter notebook is created:
You can open the notebook and simply execute the cell.
The GUI now looks like this:
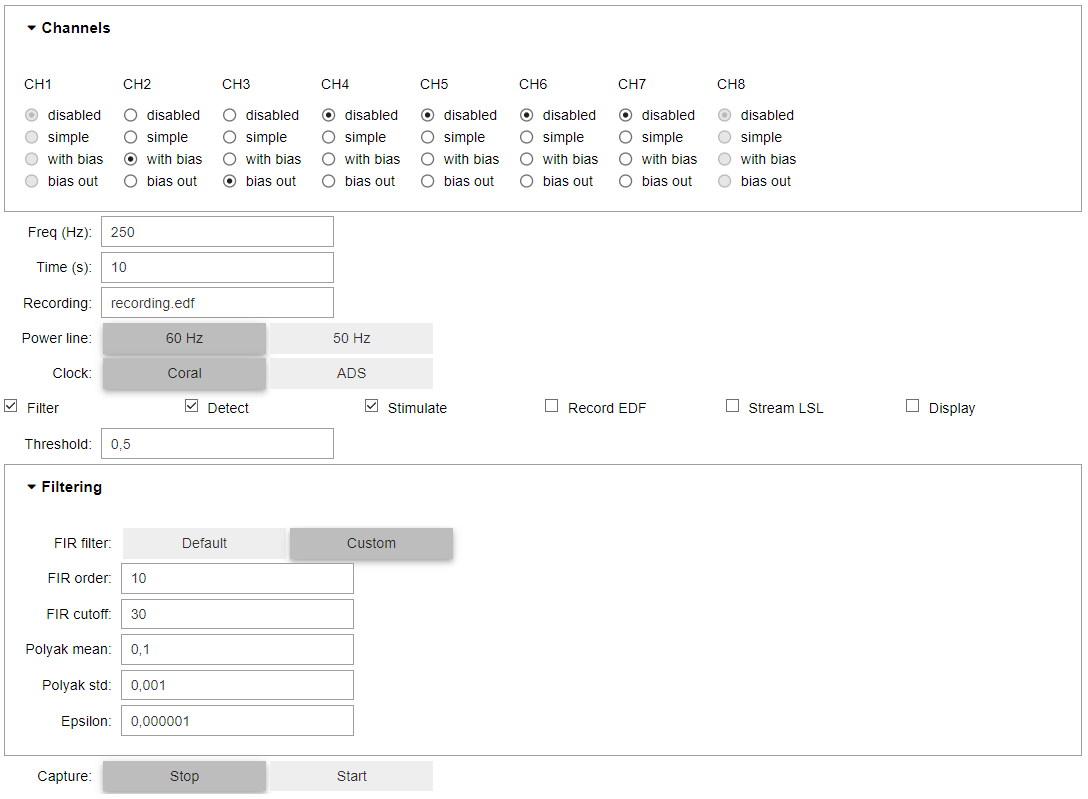
Channels:
The Channels pannel enables you to configure each electrode:
disabled: the electrode is not usedsimple: the electrode is simply used to measure signal (not recommended)with bias: the electrode is used to measure signal and to compute a bias ("ground") signalbias out: the electrode is used to output the bias ("ground") signal
General controls:
Freqis the desired sampling rateTimeis the maximum duration of the experiment (you can also stop the experiment manually)Recordingis the name of the.edfoutput file if you wish to record the signal locally- Tick
Filterto enable the online filtering pipeline - Tick
Detectto enable the online detection pipeline - Tick
Stimulateto enable the online stimulation pipeline - Tick
Record EDFto record the signal in the file designated inRecording - Tick
Stream LSLto broadcast the signal on the local network via LSL - Tick
Displayto display the signal in the GUI Thresholdenables customizing the optional detection threshold from the GUI (e.g., for classifiers)- The
Clockwidget lets you select the sampling method:Coralsets theADS1299sampling rate to twice your target sampling rate, and uses the Coral Real-Time clock to stick to your target sampling rateADSsets theADS1299sampling rate to the closest compatible to your target sampling rate and uses the ADS interrupts
Custom Filtering
The Filtering section lets you customize the filtering pipeline from the GUI.
- The
FIR filterswitch lets you select between the default low-pass FIR filter (used in the Portiloop paper), or customize this filter according to your needs (FIR orderandFIR cutoff) Polyak mean,Polyak stdandEpsilonlet you customize the online standardization pipeline, which also acts as a high-pass filter
Capture
The Capture switch lets you start and stop the experiment at any point in time
Note: once the experiment is started, all widgets are deactivated until you stop the experiment.
Installation:
Follow these instruction if the software is not readily installed on your Portiloop device.
Install the library:
(Requires python 3)
Install the following libraries from apt to avoid issues:
sudo apt install python3-numpysudo apt install python3-scipysudo apt install python3-pycoral- Clone this repository on the
Coralboard cdto he root of the repository where thesetup.pyfile is located- Execute
pip3 install -e .
Setup the Coral board as a wifi access point
You can find instructions here to set Linux as a WiFi access point.
Setup a jupyter server:
- On your
Portiloopdevice, executepip3 install notebook - Generate a
jupyterpassword and copy the result:
from notebook.auth import passwd
passwd()
- Execute
jupyter notebook --generate-config cdto the.jupyterfolder and editjupyter_notebook_config.py- Find the relevant lines, and uncomment them while setting the following values:
c.NotebookApp.ip = '*'c.NotebookApp.open_browser = Falsec.NotebookApp.password = u'your_generated_password_here'c.NotebookApp.port = 9000
Setup a service for your jupyter server to start automatically:
cd /etc/systemd/system- create an empty file named
notebook.serviceand open it. - paste the following and save:
[Unit]
Description=Autostarts jupyter server
[Service]
User=mendel
WorkingDirectory=~
ExecStart=jupyter notebook
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
- Execute
sudo systemctl daemon-reload - Execute
sudo systemctl start notebook.service - Check that your service is up and running:
sudo systemctl status notebook.service