A newer version of the Gradio SDK is available:
5.12.0
Amphion Singing Voice Conversion (SVC) Recipe
Quick Start
We provide a beginner recipe to demonstrate how to train a cutting edge SVC model. Specifically, it is also an official implementation of the paper "Leveraging Diverse Semantic-based Audio Pretrained Models for Singing Voice Conversion" (2024 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop). Some demos can be seen here.
Supported Model Architectures
The main idea of SVC is to first disentangle the speaker-agnostic representations from the source audio, and then inject the desired speaker information to synthesize the target, which usually utilizes an acoustic decoder and a subsequent waveform synthesizer (vocoder):
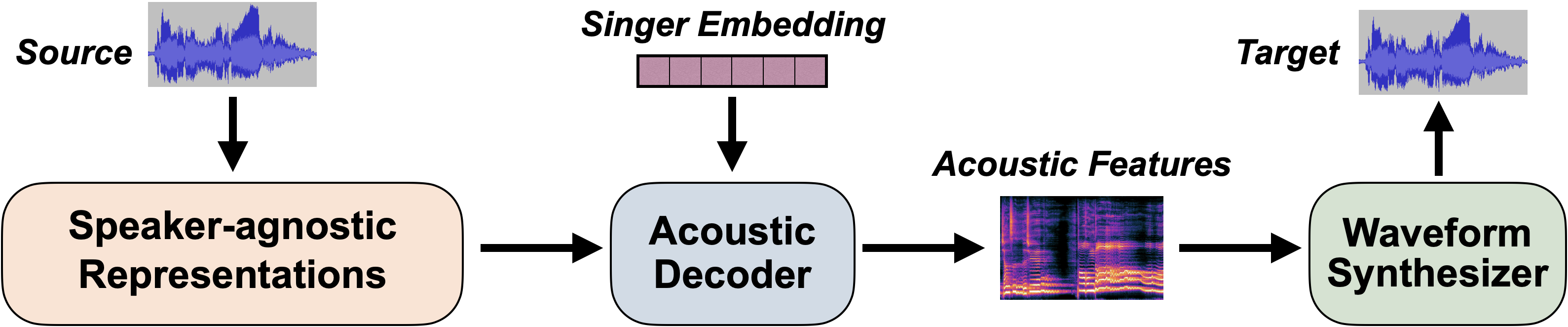
Until now, Amphion SVC has supported the following features and models:
- Speaker-agnostic Representations:
- Content Features: Sourcing from WeNet, Whisper, and ContentVec.
- Prosody Features: F0 and energy.
- Speaker Embeddings:
- Speaker Look-Up Table.
- Reference Encoder (👨💻 developing): It can be used for zero-shot SVC.
- Acoustic Decoders:
- Diffusion-based models:
- DiffWaveNetSVC: The encoder is based on Bidirectional Non-Causal Dilated CNN, which is similar to WaveNet, DiffWave, and DiffSVC.
- DiffComoSVC (👨💻 developing): The diffusion framework is based on Consistency Model. It can significantly accelerate the inference process of the diffusion model.
- Transformer-based models:
- TransformerSVC: Encoder-only and Non-autoregressive Transformer Architecture.
- VAE- and Flow-based models:
- VitsSVC: It is designed as a VITS-like model whose textual input is replaced by the content features, which is similar to so-vits-svc.
- Diffusion-based models:
- Waveform Synthesizers (Vocoders):
- The supported vocoders can be seen in Amphion Vocoder Recipe.