The Pythia Scaling Suite is a collection of models developed to facilitate interpretability research (see paper). It contains two sets of eight models of sizes 70M, 160M, 410M, 1B, 1.4B, 2.8B, 6.9B, and 12B. For each size, there are two models: one trained on the Pile, and one trained on the Pile after the dataset has been globally deduplicated. All 8 model sizes are trained on the exact same data, in the exact same order. We also provide 154 intermediate checkpoints per model, hosted on Hugging Face as branches.
The Pythia model suite was deliberately designed to promote scientific research on large language models, especially interpretability research. Despite not centering downstream performance as a design goal, we find the models match or exceed the performance of similar and same-sized models, such as those in the OPT and GPT-Neo suites.
Details on previous early release and naming convention.
Previously, we released an early version of the Pythia suite to the public.
However, we decided to retrain the model suite to address a few hyperparameter
discrepancies. This model card lists the changes;
see appendix B in the Pythia paper for further discussion. We found no
difference in benchmark performance between the two Pythia versions.
The old models are
still available, but we
suggest the retrained suite if you are just starting to use Pythia.
This is the current release.
Please note that all models in the Pythia suite were renamed in January 2023. For clarity, a table comparing the old and new names is provided in this model card, together with exact parameter counts.
Pythia-160M
Model Details
- Developed by: EleutherAI
- Model type: Transformer-based Language Model
- Language: English
- Learn more: Pythia's GitHub repository for training procedure, config files, and details on how to use. See paper for more evals and implementation details.
- Library: GPT-NeoX
- License: Apache 2.0
- Contact: to ask questions about this model, join the EleutherAI
Discord, and post them in
#release-discussion. Please read the existing Pythia documentation before asking about it in the EleutherAI Discord. For general correspondence: contact@eleuther. ai.
| Pythia model | Non-Embedding Params | Layers | Model Dim | Heads | Batch Size | Learning Rate | Equivalent Models |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70M | 18,915,328 | 6 | 512 | 8 | 2M | 1.0 x 10-3 | — |
| 160M | 85,056,000 | 12 | 768 | 12 | 2M | 6.0 x 10-4 | GPT-Neo 125M, OPT-125M |
| 410M | 302,311,424 | 24 | 1024 | 16 | 2M | 3.0 x 10-4 | OPT-350M |
| 1.0B | 805,736,448 | 16 | 2048 | 8 | 2M | 3.0 x 10-4 | — |
| 1.4B | 1,208,602,624 | 24 | 2048 | 16 | 2M | 2.0 x 10-4 | GPT-Neo 1.3B, OPT-1.3B |
| 2.8B | 2,517,652,480 | 32 | 2560 | 32 | 2M | 1.6 x 10-4 | GPT-Neo 2.7B, OPT-2.7B |
| 6.9B | 6,444,163,072 | 32 | 4096 | 32 | 2M | 1.2 x 10-4 | OPT-6.7B |
| 12B | 11,327,027,200 | 36 | 5120 | 40 | 2M | 1.2 x 10-4 | — |
Uses and Limitations
Intended Use
The primary intended use of Pythia is research on the behavior, functionality,
and limitations of large language models. This suite is intended to provide
a controlled setting for performing scientific experiments. We also provide
154 checkpoints per model: initial step0, 10 log-spaced checkpoints
step{1,2,4...512}, and 143 evenly-spaced checkpoints from step1000 to
step143000. These checkpoints are hosted on Hugging Face as branches. Note
that branch 143000 corresponds exactly to the model checkpoint on the main
branch of each model.
You may also further fine-tune and adapt Pythia-160M for deployment, as long as your use is in accordance with the Apache 2.0 license. Pythia models work with the Hugging Face Transformers Library. If you decide to use pre-trained Pythia-160M as a basis for your fine-tuned model, please conduct your own risk and bias assessment.
Out-of-scope use
The Pythia Suite is not intended for deployment. It is not a in itself a product and cannot be used for human-facing interactions. For example, the model may generate harmful or offensive text. Please evaluate the risks associated with your particular use case.
Pythia models are English-language only, and are not suitable for translation or generating text in other languages.
Pythia-160M has not been fine-tuned for downstream contexts in which language models are commonly deployed, such as writing genre prose, or commercial chatbots. This means Pythia-160M will not respond to a given prompt the way a product like ChatGPT does. This is because, unlike this model, ChatGPT was fine-tuned using methods such as Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) to better “follow” human instructions.
Limitations and biases
The core functionality of a large language model is to take a string of text and predict the next token. The token used by the model need not produce the most “accurate” text. Never rely on Pythia-160M to produce factually accurate output.
This model was trained on the Pile, a dataset known to contain profanity and texts that are lewd or otherwise offensive. See Section 6 of the Pile paper for a discussion of documented biases with regards to gender, religion, and race. Pythia-160M may produce socially unacceptable or undesirable text, even if the prompt itself does not include anything explicitly offensive.
If you plan on using text generated through, for example, the Hosted Inference API, we recommend having a human curate the outputs of this language model before presenting it to other people. Please inform your audience that the text was generated by Pythia-160M.
Quickstart
Pythia models can be loaded and used via the following code, demonstrated here
for the third pythia-70m-deduped checkpoint:
from transformers import GPTNeoXForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model = GPTNeoXForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"EleutherAI/pythia-70m-deduped",
revision="step3000",
cache_dir="./pythia-70m-deduped/step3000",
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
"EleutherAI/pythia-70m-deduped",
revision="step3000",
cache_dir="./pythia-70m-deduped/step3000",
)
inputs = tokenizer("Hello, I am", return_tensors="pt")
tokens = model.generate(**inputs)
tokenizer.decode(tokens[0])
Revision/branch step143000 corresponds exactly to the model checkpoint on
the main branch of each model.
For more information on how to use all Pythia models, see documentation on
GitHub.
Training
Training data
The Pile is a 825GiB general-purpose dataset in
English. It was created by EleutherAI specifically for training large language
models. It contains texts from 22 diverse sources, roughly broken down into
five categories: academic writing (e.g. arXiv), internet (e.g. CommonCrawl),
prose (e.g. Project Gutenberg), dialogue (e.g. YouTube subtitles), and
miscellaneous (e.g. GitHub, Enron Emails). See the Pile
paper for a breakdown of all data sources,
methodology, and a discussion of ethical implications. Consult the
datasheet for more detailed documentation
about the Pile and its component datasets. The Pile can be downloaded from
the official website, or from a community
mirror.
The Pile was not deduplicated before being used to train Pythia-160M.
Training procedure
All models were trained on the exact same data, in the exact same order. Each
model saw 299,892,736,000 tokens during training, and 143 checkpoints for each
model are saved every 2,097,152,000 tokens, spaced evenly throughout training,
from step1000 to step143000 (which is the same as main). In addition, we
also provide frequent early checkpoints: step0 and step{1,2,4...512}.
This corresponds to training for just under 1 epoch on the Pile for
non-deduplicated models, and about 1.5 epochs on the deduplicated Pile.
All Pythia models trained for 143000 steps at a batch size
of 2M (2,097,152 tokens).
See GitHub for more details on training
procedure, including how to reproduce
it.
Pythia uses the same tokenizer as GPT-NeoX-
20B.
Evaluations
All 16 Pythia models were evaluated using the LM Evaluation
Harness. You can access
the results by model and step at results/json/* in the GitHub
repository.
Expand the sections below to see plots of evaluation results for all
Pythia and Pythia-deduped models compared with OPT and BLOOM.
LAMBADA – OpenAI

Physical Interaction: Question Answering (PIQA)

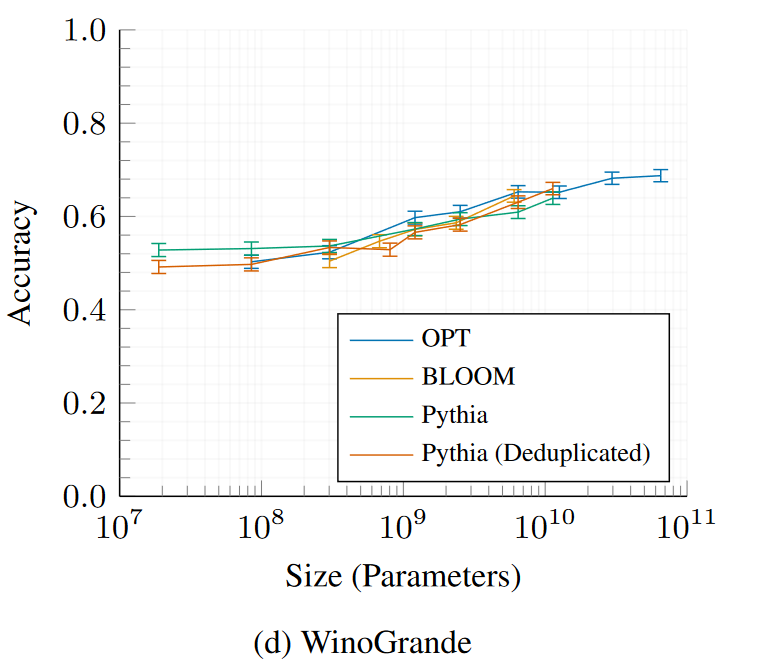
WinoGrande
AI2 Reasoning Challenge—Easy Set

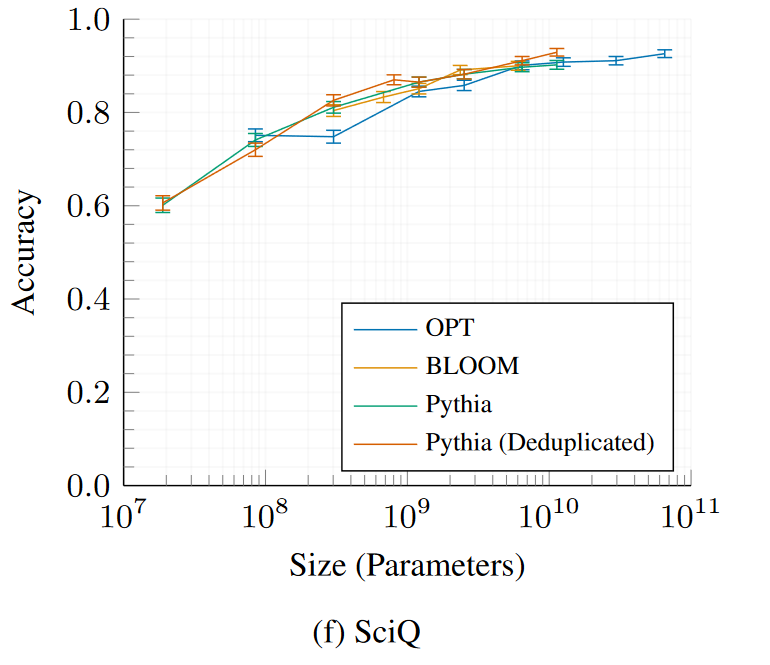
SciQ
Changelog
This section compares differences between previously released Pythia v0 and the current models. See Appendix B of the Pythia paper for further discussion of these changes and the motivation behind them. We found that retraining Pythia had no impact on benchmark performance.
- All model sizes are now trained with uniform batch size of 2M tokens. Previously, the models of size 160M, 410M, and 1.4B parameters were trained with batch sizes of 4M tokens.
- We added checkpoints at initialization (step 0) and steps {1,2,4,8,16,32,64, 128,256,512} in addition to every 1000 training steps.
- Flash Attention was used in the new retrained suite.
- We remedied a minor inconsistency that existed in the original suite: all models of size 2.8B parameters or smaller had a learning rate (LR) schedule which decayed to a minimum LR of 10% the starting LR rate, but the 6.9B and 12B models all used an LR schedule which decayed to a minimum LR of 0. In the redone training runs, we rectified this inconsistency: all models now were trained with LR decaying to a minimum of 0.1× their maximum LR.
Naming convention and parameter count
Pythia models were renamed in January 2023. It is possible that the old naming convention still persists in some documentation by accident. The current naming convention (70M, 160M, etc.) is based on total parameter count.
| current Pythia suffix | old suffix | total params | non-embedding params |
|---|---|---|---|
| 70M | 19M | 70,426,624 | 18,915,328 |
| 160M | 125M | 162,322,944 | 85,056,000 |
| 410M | 350M | 405,334,016 | 302,311,424 |
| 1B | 800M | 1,011,781,632 | 805,736,448 |
| 1.4B | 1.3B | 1,414,647,808 | 1,208,602,624 |
| 2.8B | 2.7B | 2,775,208,960 | 2,517,652,480 |
| 6.9B | 6.7B | 6,857,302,016 | 6,444,163,072 |
| 12B | 13B | 11,846,072,320 | 11,327,027,200 |
- Downloads last month
- 105,602